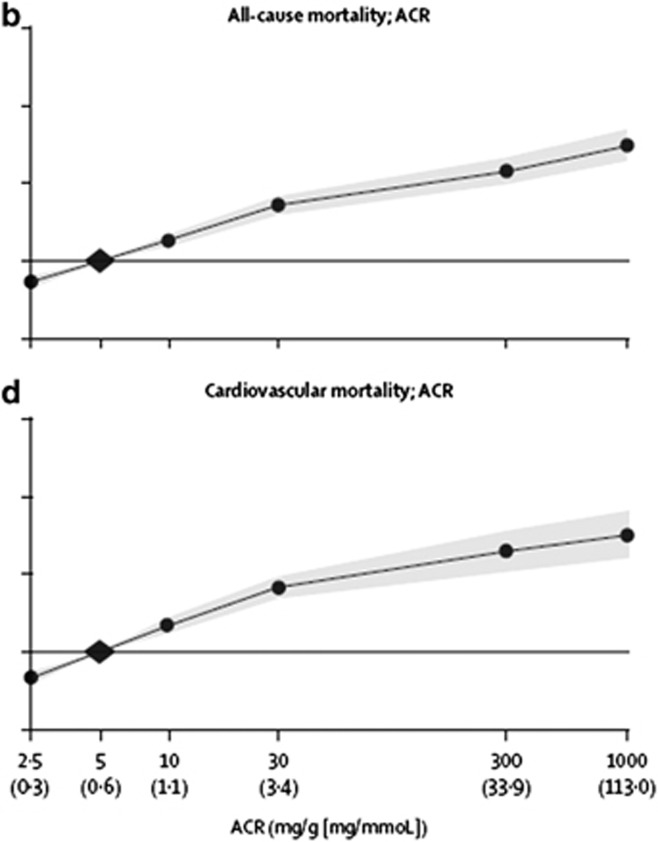
Figure 4.
Relationship of albuminuria with mortality. HRs and 95% CIs for all-cause (b) and cardiovascular mortality (d) according to ACR. HRs and 95% CIs (shaded areas) are adjusted for age, sex, ethnic origin, history of CVD, systolic BP, diabetes, smoking, and total cholesterol and spline eGFR. The reference (diamond) was ACR 5 mg/g (0.6 mg/mmol) and eGFR 95 ml/min/1.73 m2, respectively. Circles represent statistically significant and triangles represent not significant. ACR plotted in mg/g. To convert ACR in mg/g to mg/mmol multiply by 0.113. Approximate conversions to mg/mmol are shown in parentheses. ACR, albumin-to-creatinine ratio; BP, blood pressure; CI, confidence interval; CVD, cardiovascular disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HR, hazard ratio. Reprinted from The Lancet, vol 375, Matshushita K, van de Velde M, Astor BC, et al.4 Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: a collaborative meta-analysis, p. 2073-2081, 2010, with permission from Elsevier; accessed http://download.thelancet.com/pdfs/journals/lancet/PIIS0140673610606745.pdf