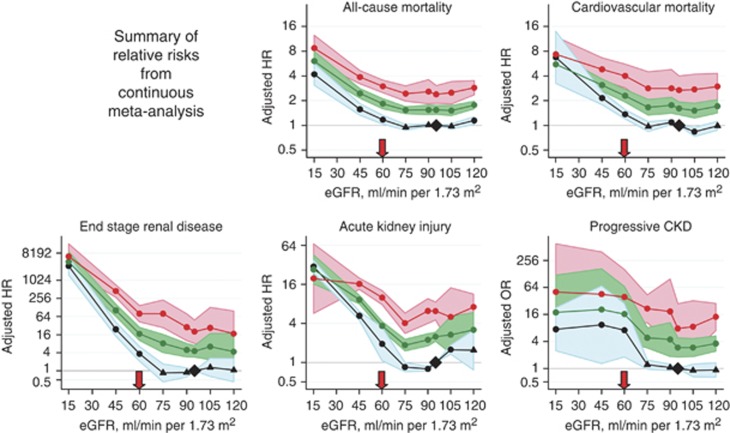
Figure 6.
Summary of continuous meta-analysis (adjusted RRs) for general population cohorts with ACR. Mortality is reported for general population cohorts assessing albuminuria as urine ACR. Kidney outcomes are reported for general population cohorts assessing albuminuria as either urine ACR or reagent strip. eGFR is expressed as a continuous variable. The three lines represent urine ACR of <30, 30-299 and ≥300 mg/g (<3, 3-29, and ≥30 mg/mmol, respectively) or reagent strip negative and trace, 1+ positive, ≥2+ positive. All results are adjusted for covariates and compared to reference point of eGFR of 95 ml/min/1.73 m2 and ACR of <30 mg/g (<3 mg/mmol) or reagent strip negative (diamond). Each point represents the pooled RR from a meta-analysis. Solid circles indicate statistical significance compared to the reference point (P <0.05); triangles indicate non-significance. Red arrows indicate eGFR of 60 ml/min/1.73 m2, threshold value of eGFR for the current definition of CKD. ACR, albumin-to-creatinine ratio; CKD, chronic kidney disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HR, hazard ratio; OR, odds ratio, RR, relative risk. Reprinted with permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Kidney International. Levey AS, de Jong PE, Coresh J, et al. The definition, classification, and prognosis of chronic kidney disease: a KDIGO controversies conference report. Kidney Int 2011; 80: 17-2830; accessed http://www.nature.com/ki/journal/v80/n1/full/ki2010483a.html