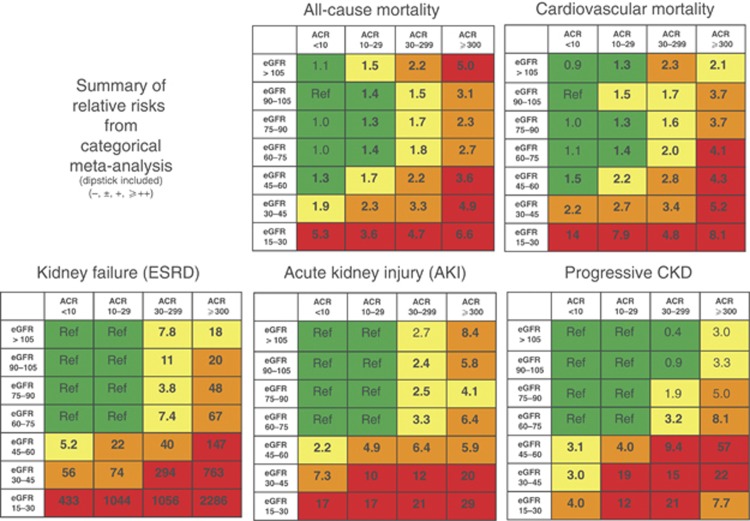
Figure 7.
Summary of categorical meta-analysis (adjusted RRs) for general population cohorts with ACR. Mortality is reported for general population cohorts assessing albuminuria as urine ACR. Kidney outcomes are reported for general population cohorts assessing albuminuria as either urine ACR or reagent strip. eGFR and albuminuria are expressed as categorical variables. All results are adjusted for covariates and compared to the reference cell (Ref). Each cell represents a pooled RR from a meta-analysis; bold numbers indicate statistical significance at P <0.05. Incidence rates per 1000 person-years for the reference cells are 7.0 for all-cause mortality, 4.5 for CVD mortality, 0.04 for kidney failure, 0.98 for AKI, and 2.02 for CKD progression. Colors reflect the ranking of adjusted RR. The point estimates for each cell were ranked from 1 to 28 (the lowest RR having rank number 1, and the highest number 28). The categories with a rank number 1-8 are green, rank numbers 9-14 are yellow, the rank numbers 15-21 are orange and the rank numbers 22-28 are colored red. (For the outcome of CKD progression, two cells with RR <1.0 are also green, leaving fewer cells as yellow, orange and red). ACR, albumin-to-creatinine ratio; AKI, acute kidney injury; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CVD, cardiovascular disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; ESRD, end-stage renal disease; RR, relative risk. Reprinted with permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Kidney International. Levey AS, de Jong PE, Coresh J, et al.30 The definition, classification, and prognosis of chronic kidney disease: a KDIGO controversies conference report. Kidney Int 2011; 80: 17-28; accessed http://www.nature.com/ki/journal/v80/n1/full/ki2010483a.html