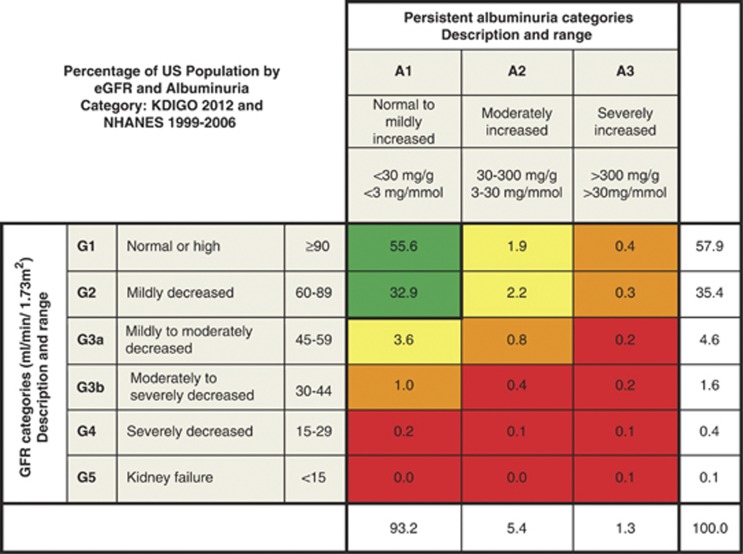
Figure 8.
Prevalence of CKD in the USA by GFR and albuminuria. Cells show the proportion of adult population in the USA. Data from the NHANES 1999-2006, N=18,026. GFR is estimated with the CKD-EPI equation and standardized serum creatinine.19 Albuminuria is determined by one measurement of ACR and persistence is estimated as described elsewhere.59 Values in cells do not total to values in margins because of rounding. Category of very high albuminuria includes nephrotic range. Green, low risk (if no other markers of kidney disease, no CKD); Yellow, moderately increased risk; Orange, high risk; Red, very high risk. ACR, albumin-to-creatinine ratio; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CKD-EPI, CKD Epidemiology Collaboration; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; NHANES, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Modified with permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Kidney International. Levey AS, de Jong PE, Coresh J, et al.30 The definition, classification, and prognosis of chronic kidney disease: a KDIGO controversies conference report. Kidney Int 2011; 80: 17-28; accessed http://www.nature.com/ki/journal/v80/n1/full/ki2010483a.html