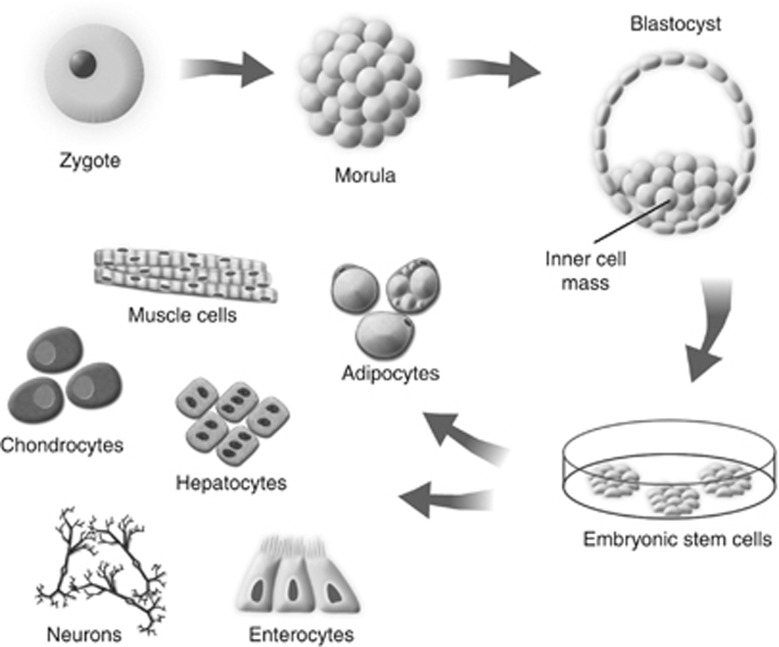
Figure 1.
Embryonic stem cell cultivation. The zygote undergoes successive mitotic divisions until a sphere of cells—the blastocyst—is formed. In the blastocyst, the trophoblast at its periphery generates the embryonic membranes and placenta, whereas the inner cell mass develops into the fetus. Embryonic stem cells are immortal in culture, having been established from one pluripotent cell collected from the inner cell mass. These are capable of differentiating into any of the mature cell types present in the adult organism.