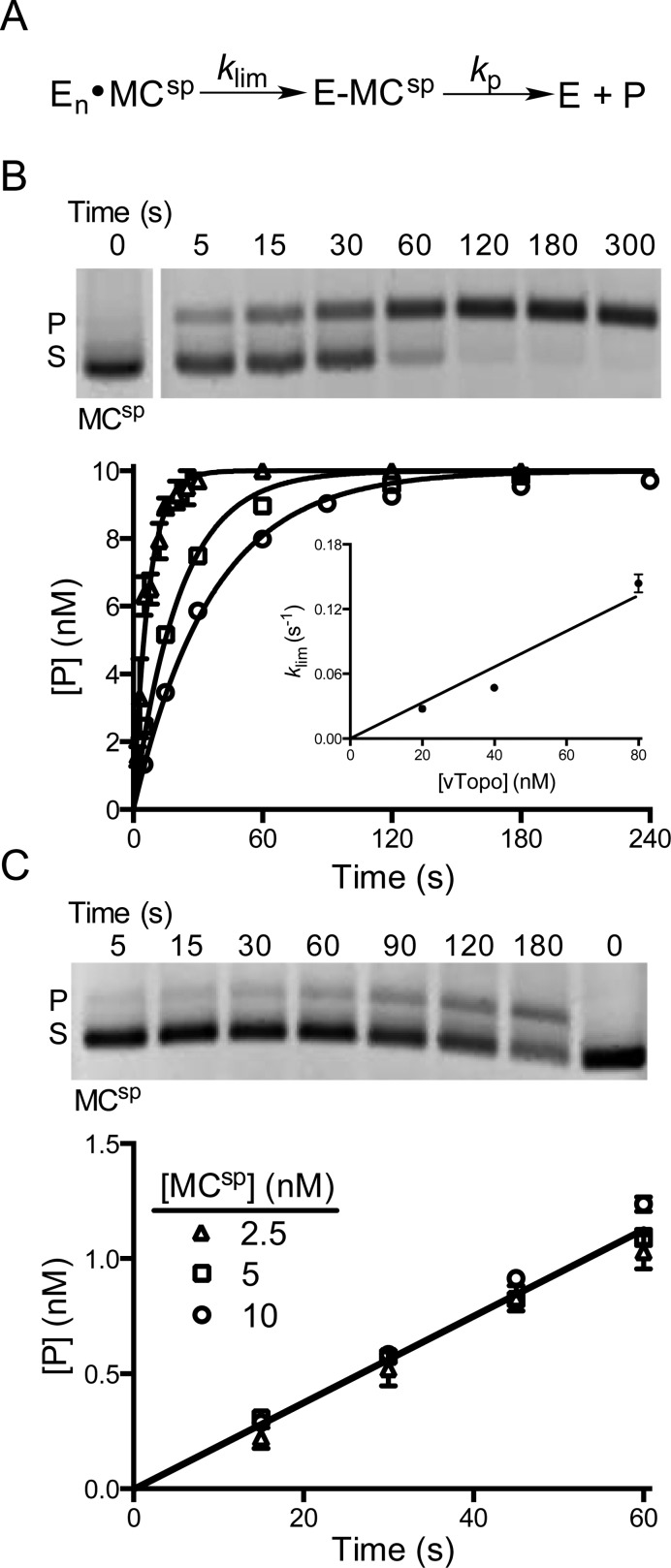
Figure 4.
Cleavage activity of vTopo with MCsp. (A) Cleavage and supercoil unwinding reactions involve a binding step, an intramolecular search mechanism, and reversible strand cleavage (klim) prior to the formation of product through supercoil unwinding (kp). (B) Single-turnover cleavage and supercoil unwinding. Supercoil unwinding of 10 nM MCsp in the presence of 20 (○), 40 (□), or 80 nM vTopo (△). The gel image shows the time course for relaxation of MCsp by 40 nM vTopo (S is the supercoiled substrate and P the relaxed product). The data were fit to a first-order rate equation for the appearance of product and confirmed using Dynafit 3. The values of klim were plotted against enzyme concentration and gave a linear response with respect to enzyme concentration over the accessible range (inset). Some error bars have been omitted for the sake of clarity but are similar to those shown. (C) Steady-state turnover under initial rate conditions. The relaxation of 5 nM MCsp in the presence of 1 nM vTopo is shown in the gel image. The rate was independent of DNA concentration in the range from 2.5 to 10 nM, indicating that the enzyme is saturated with DNA and the maximal steady-state velocity is being measured.