Fig. 1.
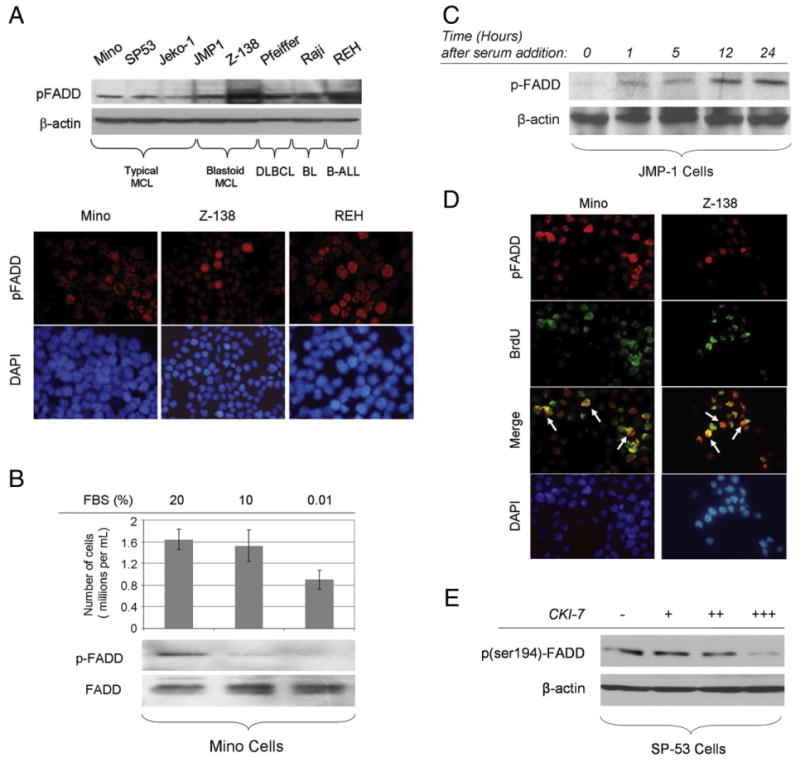
A, ser194p-FADD is expressed in B-cell NHL cell lines tested at variable levels (upper panel). ser194p-FADD protein is detected in the nucleus of Mino, Z-138, and REH cells using immunofluorescence in cytospin preparations (lower panel). B, Mino cells were incubated in 20% (control), 10%, or 0.01% FBS for 24 hours. Western blot analysis shows that the levels of ser194p-FADD expression are diminished after 24 hours of serum starvation. The total number of viable cells per volume (in milliliters) is decreased following serum deprivation. C, JMP-1 cells were initially serum starved for cell synchronization, then incubated with FBS, and collected at various time points. The expression levels of ser194p-FADD increased gradually over time in these synchronized cells. D, Mino and Z-138 cells were incubated with BrdU for 1 hour at 37°C, and double immunofluorescence was performed using cytospin preparations, antibodies specific for ser194p-FADD and BrdU, and DAPI as counterstain. ser194p-FADD and BrdU were detected using different secondary antibodies visible as red and green, respectively. A subset of cells was positive for both ser194p-FADD and BrdU as shown with yellow color in merged images, indicating that FADD phosphorylation at serine 194 is more prominent in the BrdU incorporating (proliferating) cell fraction (white arrows). E, Incubation of proliferating SP-53 cells, growing in 15% FBS, with increasing concentrations of the CKIα-specific inhibitor, CKI-7, up to 250 μmol/L for 8 hours, resulted in gradual decrease of ser194p-FADD levels, as shown by Western blot analysis.
