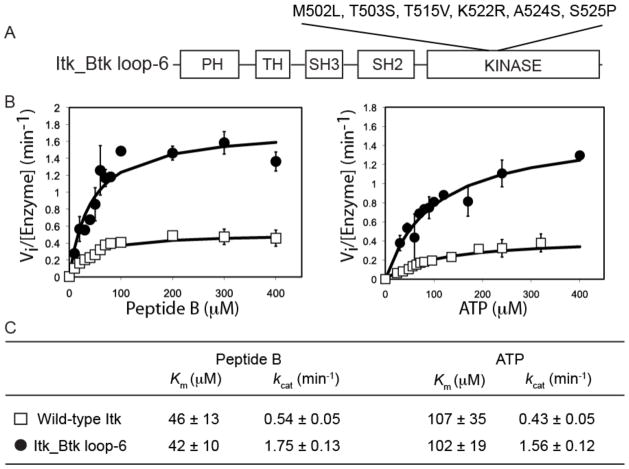
Fig. 3. Kinetic analysis of full-length Itk and the full-length Itk_Btk loop-6 protein.
(A) Substitution of the indicated six amino acid residues in the activation segment of Itk with those of Btk was required to create the full-length Itk_Btk loop-6 mutant. The N-terminal regulatory domains of full-length Itk or Itk_Btk loop-6 proteins consists of an N-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, followed by a Tec homology (TH) domain, and Src homology (SH) domains SH3 and SH2. (B) Peptide B and ATP substrate curves comparing the in vitro phosphorylation kinetics of wild-type Itk (open squares) and the Itk_Btk loop-6 mutant (filled circles). The magnitude of the activity increase for full-length Itk_Btk loop-6 compared to that of full-length WT Itk was less than that observed for the corresponding WT and mutant isolated kinase domain fragments (Fig. 1B), whereas the overall activity (Vi value) was higher for the full-length proteins as compared to the Vi of the isolated kinase domain fragments. (C) Kinetic constants for the WT Itk and Itk_Btk loop-6 proteins were derived from two independent experiments. Error bars represent SD from the mean.