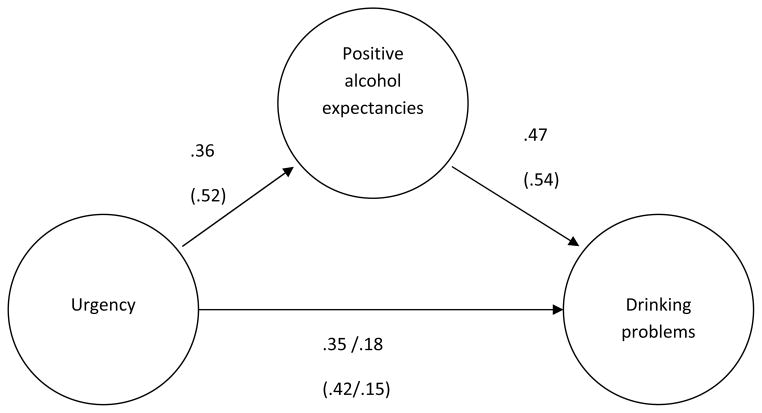
Figure 2.
SEM test of Positive alcohol expectancies mediating the relationship between urgency and drinking problems in First Nation people and Caucasians. For each path, the first number represents the path estimate for First Nation people and the second number (in parentheses) for Caucasians. For the urgency to drinking problems path, the two coefficients not in parentheses apply to First Nation people and represent, first, the association between negative urgency and drinking problems without considering alcohol expectancies, and then, after the slash, the association between negative urgency and drinking problems with alcohol expectancies included in the model. The coefficients in parentheses apply to Caucasians, and again, the first coefficient is between negative urgency and drinking problems without alcohol expectancies in the model and the second coefficient reflects the same association with expectancies included. Path coefficients represent maximum likelihood estimates.