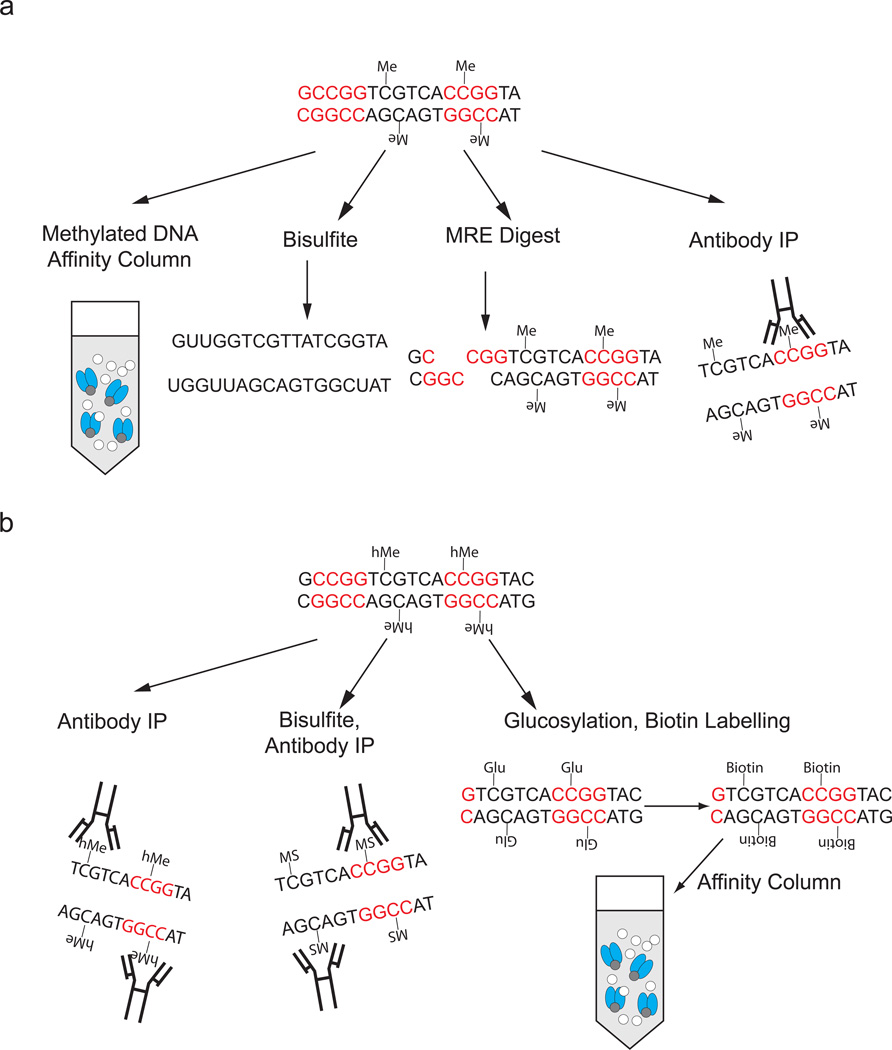
Figure 1.
A summary of methods for direct detection of cytosine methylation and hydroxymethylation. (a) Methylated DNA can be detected with methyl-sensitive restriction enzymes (MRE), the use of antibodies specific for 5-methylcytosine (5MC), by binding to affinity columns that contain methylated DNA binding domains or by the conversion of DNA with sodium bisulfite. It is important to note that some methyl-sensitive restriction enzymes are also sensitive to hydroxymethylation. (b) Several methods have been developed to detect 5 hydroxymethylcytosine (5HMC). These include the addition of a biotin tag to 5HMC through glucosylation and subsequent chemical steps which is followed by an affinity pulldown of the biotin tag, the use of antibodies specific for 5HMC and conversion of 5HMC to 5-cytosine methylenesulfonate (MS) which is then immunoprecipitated with an antibody specific to 5CMS. Me = Methylated Cytosine. hMe = hydroxymethylated cytosine. Glu = glucosylated cytosine.