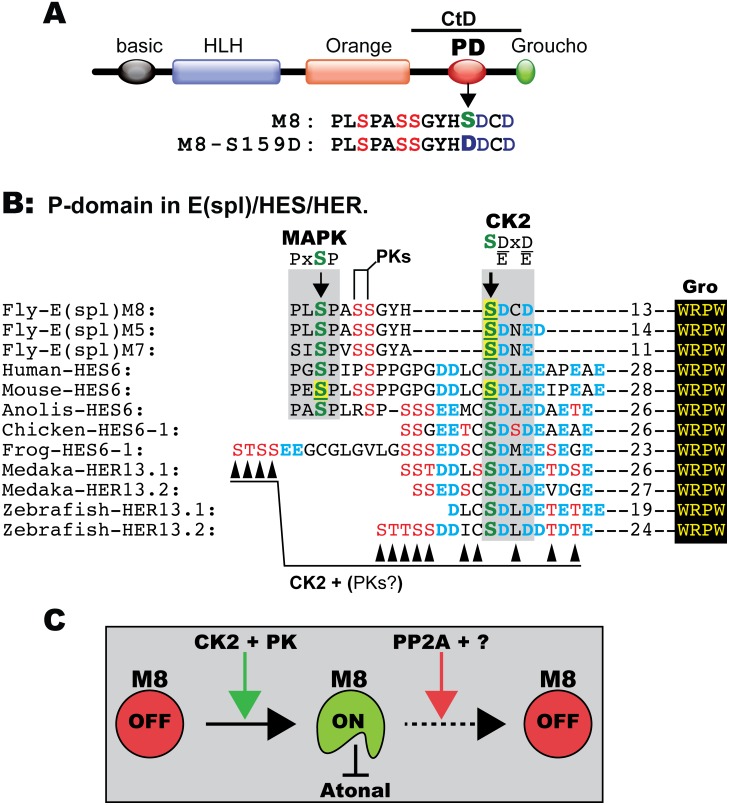
Figure 7. Conserved Ser residues in E(spl)/HES/HER and model for regulation of M8.
(A) Functional domains in E(spl) proteins; the red oval is the Ser-rich phosphorylation domain (PD) located in the C-terminal domain (CtD). The P-domain of M8 and its CK2 mimetic form M8-S159D. (B) Alignment of the P-domain in Drosophila E(spl)-M8, -M5, -M7, HES6 from mammals/reptiles/birds/frogs, and the fish HER13 isoforms. The consensus sites for CK2 and MAPK are shown. Note the invariant CK2 site in E(spl)/HES/HER. The underlined Ser residues highlighted in yellow denote biochemically identified CK2 and MAPK sites. Arrowheads below alignment denote residues predicted to also be modified by CK2, and PK denotes yet unidentified protein kinases. The number of residues separating the P-domain from the C-terminal WRPW motif is indicated. (C) Model for regulation of M8. CK2 in concert with other protein kinases (PK) converts M8 into an active repressor of Atonal, whereas PP2A in concert with yet unidentified factors (?) mediate inactivation, through a conformational change or by destruction.