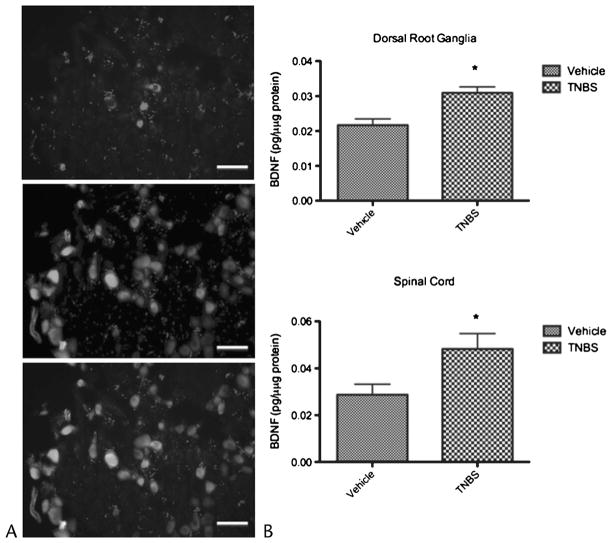
FIGURE 1.
Chronic pancreatitis results in up-regulation of BDNF in sensory nerves. A, Cryosections of thoracic DRGs were fluorescently stained for BDNF presence. Representative picture of BDNF-positive neurons in a DRG section (top panel) and DiI-labeled pancreas-specific neurons (middle panel). The bottom panel shows a merged picture identifying both pancreas specific BDNF expressing neurons. Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid–treated animals had a significantly higher percentage of BDNF-expressing pancreas-specific neurons compared to controls (50.9% vs 43.2%, P < 0.05). Scale bar, 50 μm. B, Levels of BDNF protein as measured by ELISA in thoracic T9-13 DRGs (top panel) and spinal cord (bottom panel) were also significantly higher in TNBS rats compared with controls (P < 0.006 vs P < 0.05, respectively).