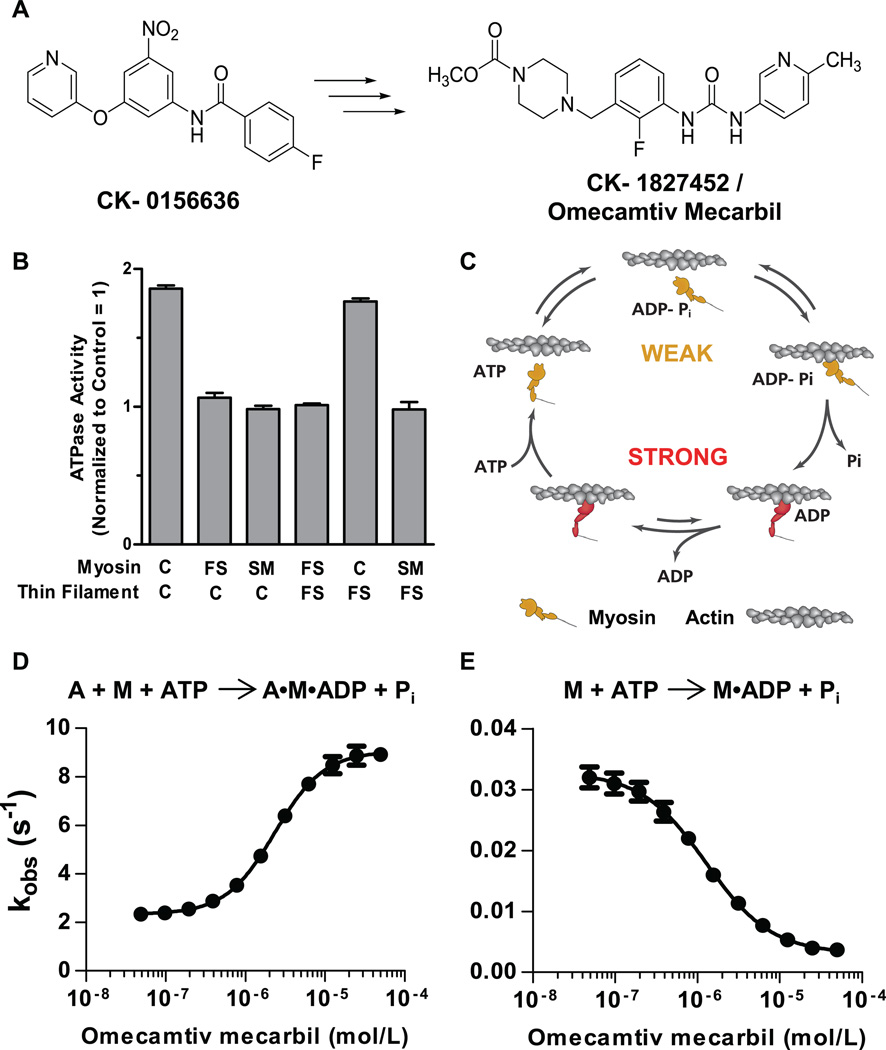
Fig. 1.
Identification and characterization of omecamtiv mecarbil. (A) The chemical structure of the original hit, CK-0156636, and the chemical structure of omecamtiv mecarbil whose optimization and synthesis have been previously reported (7). (B) Target identification of omecamtiv mecarbil using heterologous reconstituted combinations of the troponin-tropomyosin regulated actin-myosin system. Means ± SD are shown for three to five replicates at each condition. ATPase measurements were made at 25°C in 12 mM Pipes, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM dithiothreitol at pH 6.8 and pCa 6.75 by using a coupled enzyme system consisting of pyruvate kinase and lactate dehydrogenase and monitoring the oxidation of NADH at 340 nM (14). C, FS, and SM denote cardiac, fast skeletal, and smooth muscle myosin isoforms. Similarly, C and FS denote reconstituted cardiac and fast skeletal thin filaments, respectively. (C) The mechanochemical cycle of myosin. Yellow indicates myosin weakly bound to actin and red indicates myosin strongly bound to actin (adapted from an illustration, courtesy of J. Spudich, Stanford University). The effect of omecamtiv mecarbil on the phosphate release rate is shown for actin (A) plus myosin (M) in panel (D) and of myosin alone in panel (E). Transient-state kinetic measurements of phosphate release from cardiac myosin S1 (n = 3 for each data point, means ± SD) were carried out by rapidly mixing a solution of myosin and ATP with 7-diethylamino-3-({[(2-maleimidyl)ethyl]amino}carbonyl) coumarin–modified phosphate-binding protein (MDCC-PBP) plus or minus actin with a stopped-flow apparatus under single-turnover conditions at 25°C. Phosphate released from myosin binds rapidly to MDCC-PBP, which leads to an increase in its fluorescence (13). The rate of phosphate release is measured at various concentrations of omecamtiv mecarbil to construct a dose response.