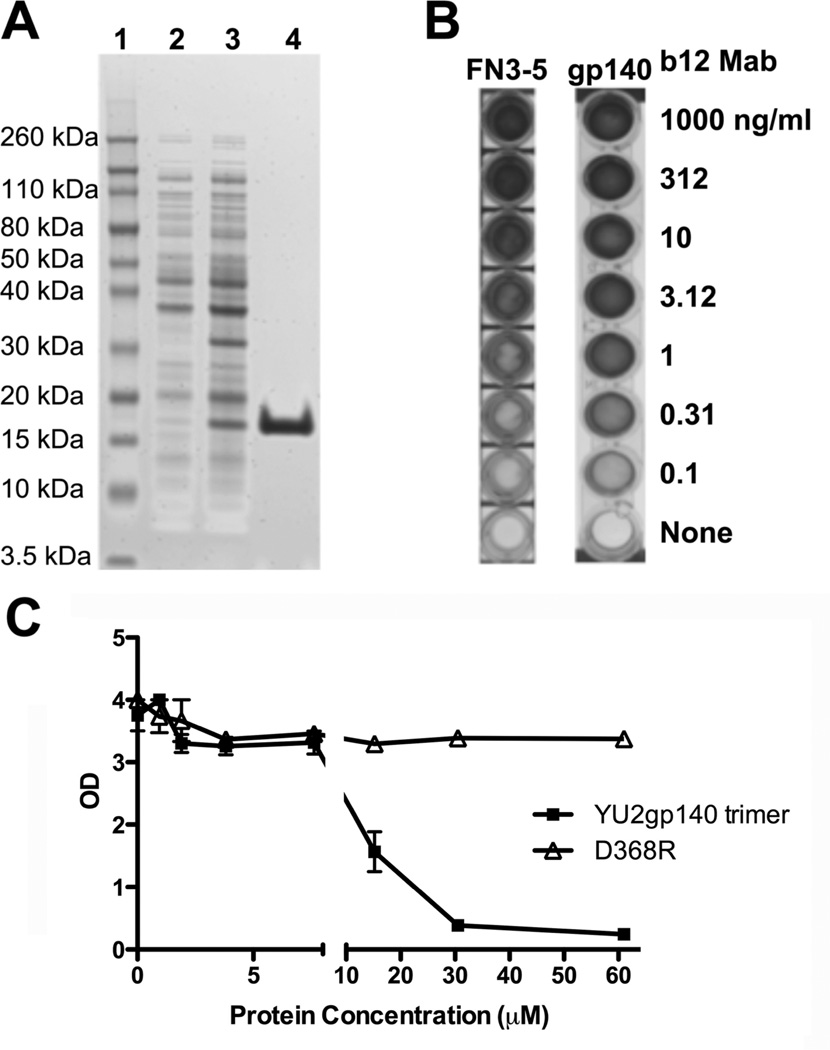
Fig 4.
Binding of purified b12 αIMs to the b12 MAb is competitively inhibited by HIV-1 Env. (A) The b12 3–5 αIM was expressed in E coli BL21 DE3 cells. A 4–12% Bis-Tris gel was loaded with samples of the uninduced culture (Lane 2), induced culture (Lane 3), and the purified eluate collected after column purification of the b12 αIM (Lane 4); Lane 1 contains molecular weight markers. (B) ELISA analysis of the binding of serially diluted b12 MAb to biotinylated b12 3–5 αIM (5µg/mL) and HIV-1 Env gp140 oligomers [42]. (C) b12 MAb (1 µg/ml) was pre-incubated with varying amounts of wild type HIV-1 Env gp140 oligomers or mutant gp140 oligomers (D368R; this lacks the ability to bind to b12) and then added to the wells coated with b12 3–5 αIM. The b12 3–5 αIM competitively inhibits binding of the b12 MAb to HIV-1 Env gp140 oligomers.