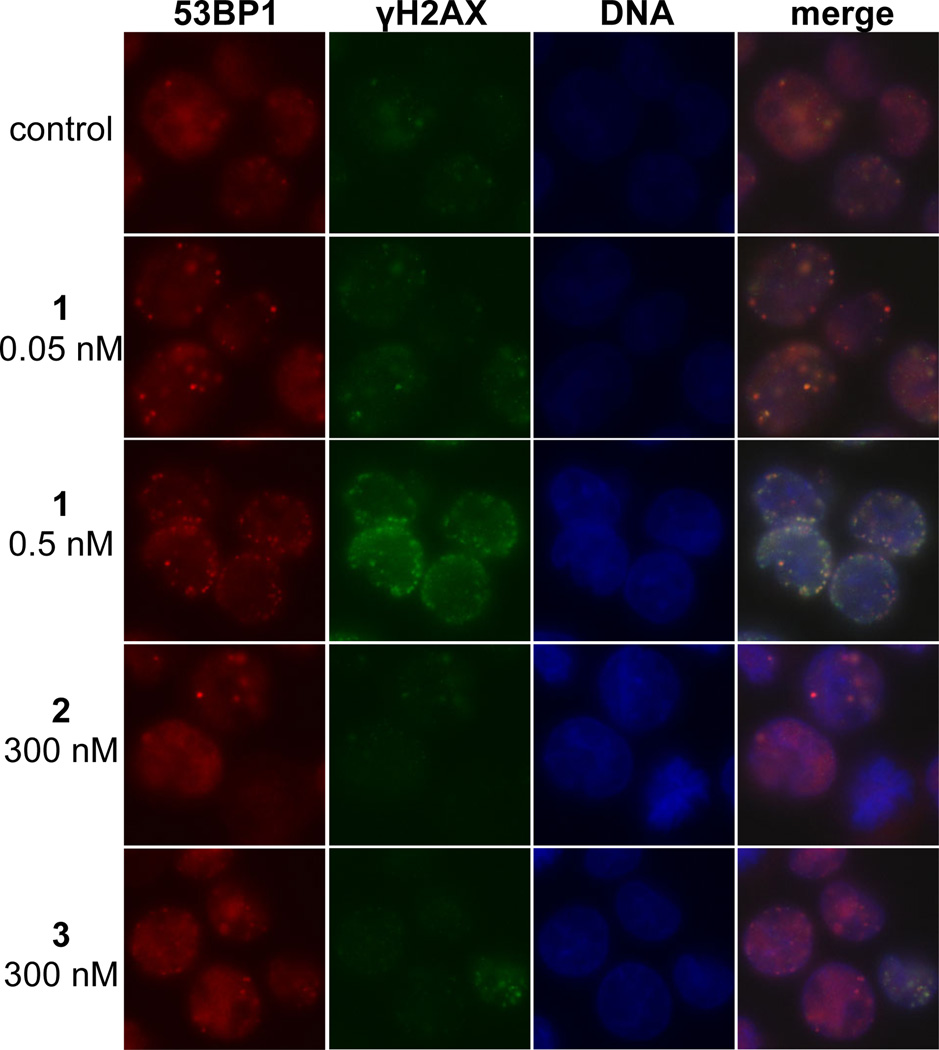
Figure 3.
Immunofluorescence imaging of γH2AX and 53BP1 foci in K562 cells treated with (–)-lomaiviticin A (1), (–)-lomaiviticin C (2), or (–)-kinamycin C (3). γH2AX and 53BP1 are commonly used markers (refs. 31–33) for DNA dsbs. Immunofluorescence imaging shows that these foci are induced and colocalize in K562 cells treated with 1 (0.05–0.5 nM), but are sparse or undetectable in cells treated with 300 nM 2 or 3. Columns (left to right), 53BP1 (red), γH2AX (green), nucleus (blue), merge. Rows (top to bottom): control, 0.05 nM 1, 0.5 nM 1, 300 nM (–)-lomaiviticin C (2), 300 nM (–)-kinamycin C (3). K562 cells in exponential growth phase were incubated with 0.05 nM 1, 0.5 nM 1, 300 nM 2, or 300 nM 3 for 4 h. Immunological detection was performed using a primary antibody [rabbit polyclonal anti-53BP1 antibody (Novus Biologicals) and mouse monoclonal anti-phospho-histone H2AX (SER139) antibody (Upstate)] and visualized with Alexa 488 (goat-anti-mouse IgG) and Alexa 594 (goat-anti-rabbit IgG). Mounting medium contained DAPI to visualize nuclear DNA.