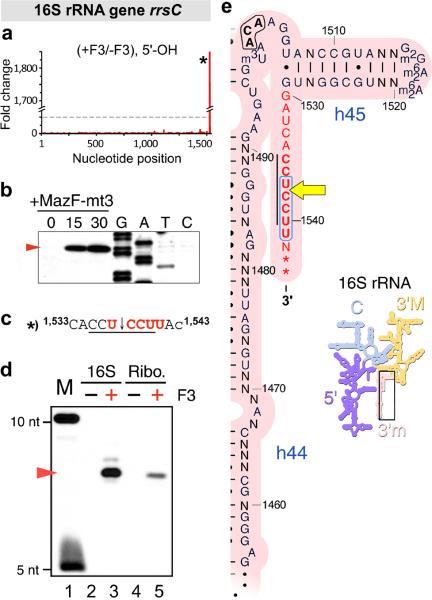
Figure 5. MazF-mt3 cleaves within the aSD sequence, both in 16S rRNA and in ribosomes.
(a) Histogram representing the ratio of #5’-ends observed in the analysis of 5’-OH from cells that did contain (+F3) or did not contain (-F3) MazF-mt3 within the E. coli 16S rRNA gene rrsC. The lone cleavage site is labeled with an asterisk (*). (b) Primer extension analysis of E. coli 16S rRNA. (c) The RNA sequence surrounding the cleavage site identified by MORE RNA-seq (a) and primer extension analysis (b), with uppercase letters denoting nucleotides in the mature 16S rRNA and the final lowercase letter depicting the first nucleotide of the downstream intergenic region. (d) 3’-end-radiolabeled E. coli 16S rRNA (16S) or 70S ribosomes (Ribo.) were incubated with (+) or without (-) purified MazF-mt3. The red arrow corresponds to ã6-nt RNA fragment generated by MazF-mt3 cleavage. Marker lane (M) contains a mixture of 10-nt and 5-nt RNA oligonucleotides, each containing a 5’-end-radiolabel. Complete gel images for (b, d) are shown in Supplementary Fig. 5. (e) Secondary structure of a conserved region of the 3’ tail (above) of 16S rRNA (inset to the lower right). The 3’ tail, whose nucleotides are highlighted in red text, is identical between E. coli and M. tuberculosis with the exception of two additional bases in M. tuberculosis at the very 3’ end, indicated with asterisks (*), and a single nonconserved base (N). E. coli position number is adjacent to tick marks, the E. coli MazF recognition sequence (ACA) is in bold black text, the aSD sequence (CCUCCU) is in bold red text with a black line to the left, the MazF-mt3 recognition sequence (UCCUU) is in bold red text encircled by a blue line, and the site cleaved by MazF-mt3 is indicated by a yellow arrow. 5’, 5’ domain of 16S rRNA; C, central domain; 3’M, 3’ major domain; and 3’m, 3’ minor domain; h44, helix 44; h45, helix 45. Images in panel (e) are adapted with permission from http://rna.ucsc.edu/rnacenter/ribosome_images.html , Center for Molecular Biology of RNA, University of California, Santa Cruz.