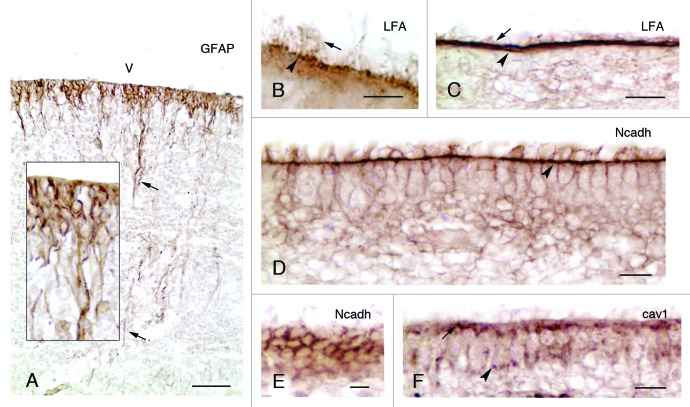
Figure 1. Development and properties of the multiciliated ependyma in the lateral ventricle of human fetuses. (A, insert) In a fetus at 23 wk of gestation, radial glial cells are observed that display long basal processes (arrows) and express GFAP. (B and C) In fetuses at 25 and 36 wk of gestation, multiciliated ependymal cells are already appreciated (arrows point to cilia) and present sialic acid at their apical pole (arrowheads), which is detected with an antibody against the Limax flavus agglutinin (LFA). (D-F) Mature multiciliated ependymal cells in a fetus at 30 wk of gestation. N-cadherin (Ncadh) is observed in transversal (D) and tangential sections (E) arranged in cell junctions (arrowhead in D). (F) Caveolin (cav1) is present in the apical pole (arrow) and basal processes (arrowhead) of mature multiciliated ependymal cells in a fetus at 30 wk of gestation. Abbreviations, v, ventricle lumen. Bars: A, 50 µm; B, 5 µm; C, E, F, 10 µm; D, 20 µm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.