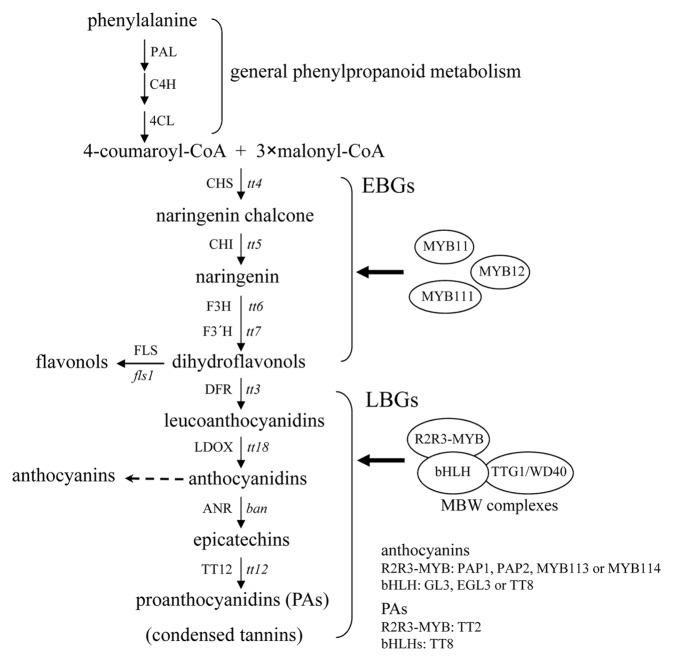
Figure 1. The biosynthetic pathway for flavonols, anthocyanins, and PAs in Arabidopsis. This pathway starts with the general phenylpropanoid metabolism and subsequent steps are catalyzed by a series of structural enzymes leading to the biosynthesis of 3 final end products, including flavonols, anthocyanins, and PAs. The early biosynthetic genes (EBGs) are activated by 3 functionally redundant R2R3-MYB proteins (MYB11, MYB12, and MYB111), whereas the expression of the late biosynthetic genes (LBGs) requires the transcriptional activation activity of the R2R3-MYB/bHLH/WD40 (MBW) complex. Enzymes are denoted in uppercase and corresponding genetic loci are indicated in italic lowercase letters. PAL, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase; C4H, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; 4CL, 4-coumarate:CoA ligase; CHS, chalcone synthase; CHI, chalcone isomerase; F3H, flavanone 3-hydroxylase; F3′H, flavanone 3′-hydroxylase; DFR, dihydroflavonol 4-reductase; LDOX, leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase; ANR, anthocyanidin reductase; tt, transparent testa; ban, banyuls.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.