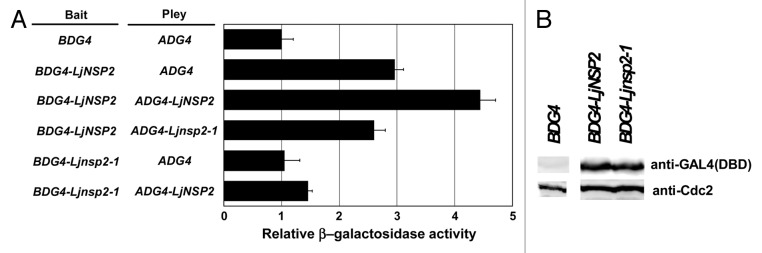
Figure 1. Yeast-two hybrid analyses of LjNSP2 interactions and immunoblotting in yeast cells. (A) Transcription activity of LacZ (β-galactosidase) was measured as the indicator of the interaction between 2 components fused with the prey (ADG4: activation domain of GAL4) and bait (BDG4: DNA binding domain of GAL4). However, an about 3-fold increase of the activity was seen with the combination BDG4-LjNSP2/ADG4 compared with control combination BDG4/ADG4, while there was no increase with BDG4-Ljnsp2–1/ADG4, indicating the presence of a transcription activity of LjNSP2 alone bound to the promoter of LacZ depending the function of the SH2-like domain. A further 50% of increase of the activity was seen in the combination BDG4-LjNSP2/ADG4-LjNSP2, being consistent with the ability of LjNSP2 to form homodimer. This is also dependent on the SH2-like function because this increase was not observed for the combination with ADG4-Ljnsp2–1. (B) Yeast transformants carrying pBD and pAD-LjNSP2, pBD-LjNSP2 and pAD-LjNSP2, pBD-Ljnsp2–1, and pAD-LjNSP2 were grown in YPD medium to late-log phase at 30 °C, cell extracts were prepared and immunoblotted by probing with anti-GAL4 (DBD) or anti-PSTAIRE antibody. The size of the detected proteins is consistent with a predicted pBD-LjNSP2 molecular mass of 71 kD. Cdc28 bands served as the internal control.
