Figure 2.
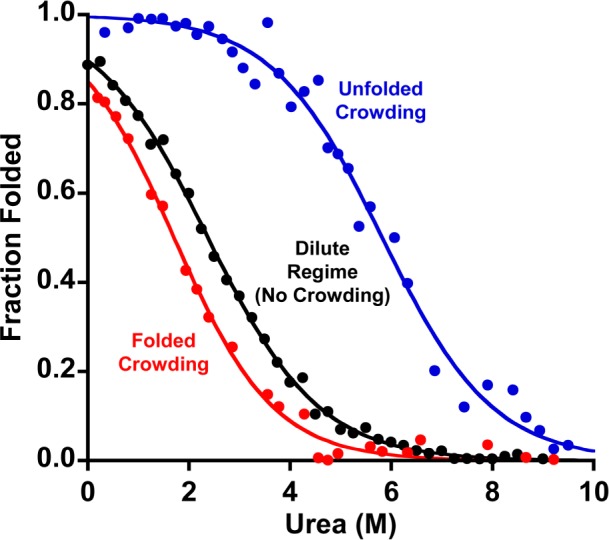
In bulk solution, crowding generally stabilizes the more compact native state.9,16,17 On a surface, in contrast, crowding is more complex. Shown is the urea-induced unfolding of a methylene-blue-modified stem-loop (in the dilute regime, i.e., with each too far, on average, from its like neighbors to interact) when (red) crowded with a highly stable stem-loop that remains folded throughout the experiment, (black) in the dilute regime (no crowding), or (blue) when crowded with a polythymine construct that remains unfolded throughout the experiment. Whereas crowding by other folded stem-loops is destabilizing (by ∼2 kJ/mol), crowding by unfolded chains strongly stabilizes the folded stem-loop (by ∼6 kJ/mol). Of note, neither of these crowding regimes alters the width of the unfolding transition, which is a measure of the m value (i.e., denaturant strength): the best-fit m values in all three regimes are within error of the 2.1 kJ/mol/M value seen in (dilute) bulk solution.1
