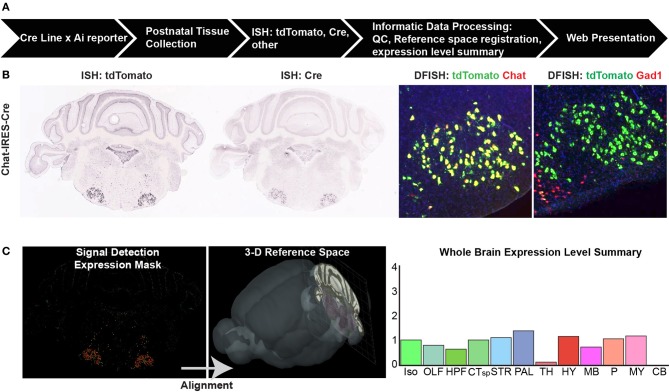
Figure 1.
Cre characterization data types and processing pipeline. (A) An overview of the high-throughput pipeline starting with crosses of mice from every characterized Cre line to a Cre reporter strain (e.g., Ai9, Ai14) to generate double positive mice for brain collection at up to four postnatal ages. The entire brain is sectioned and tissue subjected to in situ hybridization (ISH) before informatics data processing and web presentation. (B) Types of ISH data collected. For every Cre/reporter line, ISH was used to detect the tdTomato reporter gene at P56. For most Cre lines, additional data types include ISH to detect the Cre gene itself at P56, and double-fluorescent ISH (DFISH) using probes for the tdTomato gene and corresponding endogenous gene to the Cre line promoter or to another cell type marker (e.g., Gad1 for inhibitory neurons). Image series throughout the rostral-caudal extent of the brain were collected to gather whole brain expression patterns. (C) Informatics data processing includes signal detection, quantification, and registration of each image series into the 3D Allen Reference Atlas (ARA) space to assign signal (expression energy) to all annotated brain regions within the ARA. A whole brain expression summary is presented online at a coarse level across 12 major brain divisions along with the image series for each brain. Abbreviations are Iso, isocortex; OLF, olfactory areas; HPF, hippocampal formation; CTsp, cortical subplate; STR, striatum; PAL, pallidum; TH, thalamus; HY, hypothalamus; MB, midbrain; P, pons; MY, medulla; and CB, cerebellum.