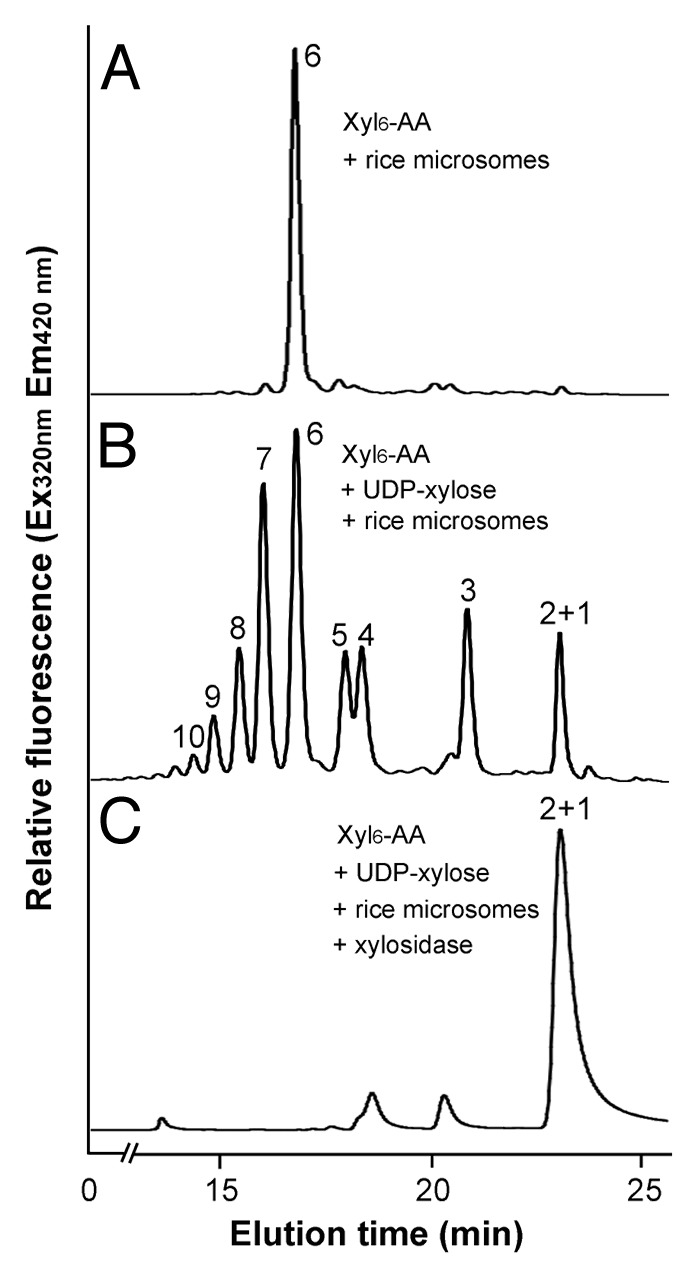
Figure 4. Digestion of the xylosyltransferase-catalyzed reaction products by β-1,4-xylosidase. Microsomes were incubated with the fluorescent Xyl6-AA acceptor and UDP-xylose. The reaction products were digested with β-1,4-xylosidase and then analyzed by reverse-phase HPLC. (A) The control reaction without UDP-xylose showing the Xyl6-AA acceptor peak. (B) Rice microsomes possess the xylosyltransferase activity capable of adding xylosyl residues onto the Xyl6-AA acceptor peak. (C) β-1,4-Xylosidase digestion of the reaction products from (B) results in their degradation into Xyl1-AA and Xyl2-AA, indicating that the reaction products are β-1,4-linked. The number at each peak denotes the number of xylosyl residues for the corresponding xylooligomer.
