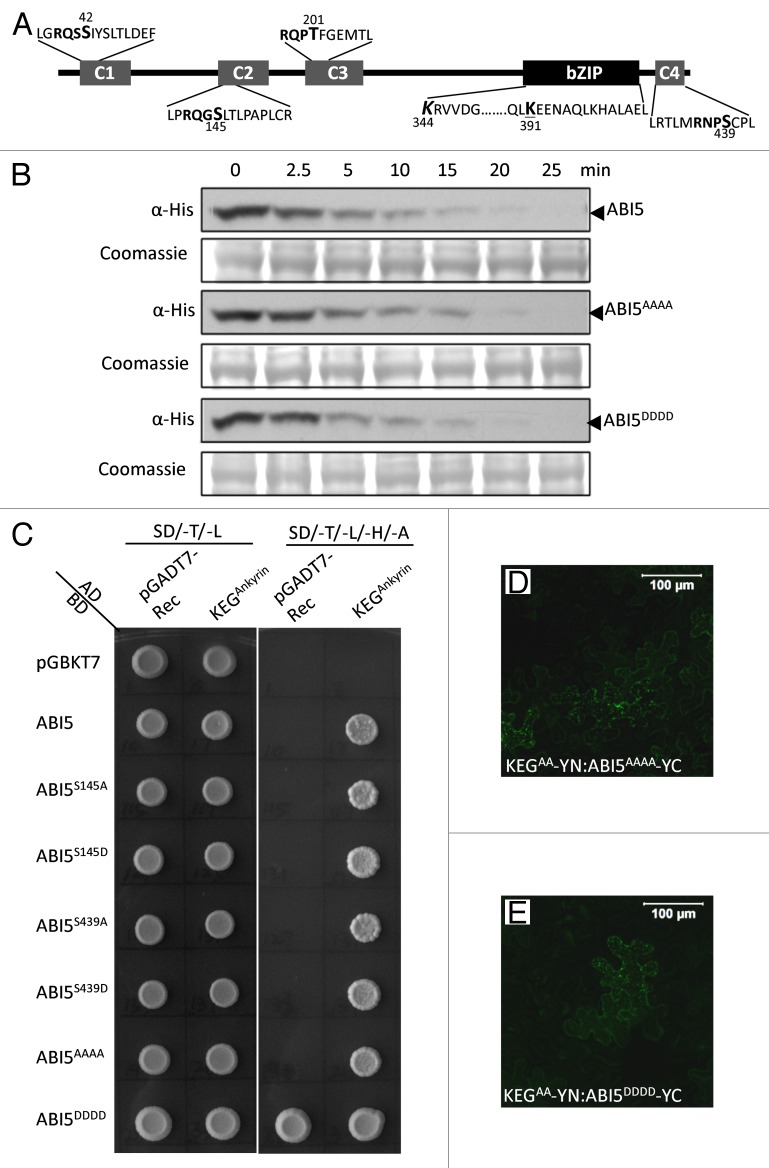
Figure 1. Phosphorylation does not impact ABI5 turnover and interactions with KEG E3 ligase. (A) Schematic representation of ABI5 showing the conserved regions, C1 - C4, and basic leucine zipper (bZIP) domain. Lysine (K) residues linked to ubiquitination (K344, bold and italics) and sumoylation (K391, bold and underlined) are highlighted. Phosphorylation sites within each conserved region (C1-C4) are shown in bold. Phosphoamino acids (serine [S] and threonine [T]) that were changed to alanine (A) or asparagine (D) are indicated (larger font and numbered). (B) Cell-free protein degradation assays. Phosphorylation sites in all 4 conserved domains (ABI5AAAA and ABI5DDDD) of ABI5 were mutated to A or D. Recombinant Flag-His tagged ABI5, ABI5AAAA and ABI5DDDD were incubated with protein extracts prepared from wild type Arabidopsis seedlings. Samples were taken at the indicated times and the level of ABI5 proteins determined by western blotting using His antibodies. Coomassie staining was used to confirm equal loading. (C) Yeast-2-hybrid experiments showing interactions between KEG and a series of ABI5 phosphomutants. Phosphorylation sites in the C2 (ABI5S145A and ABI5S145D), C4 (ABI5S439A and ABI5S439D), or all 4 conserved domains (ABI5AAAA and ABI5DDDD) of ABI5 were mutated to A or D. ABI5 cDNA constructs were fused to the GAL4 binding domain (BD) and KEG cDNA encoding for the ankyrin repeats (KEGAnkyrin) was fused to the GAL4 activating domain (AD). Interaction was analyzed by growth on selection medium without Trp, Leu, His, and Ade (SD/-T/-L/-H/-A). ABI5DDDD produced a high level of autoactivation. The pGADT7 and pGBKT7-Rec empty vectors were used as negative controls. (D-E) BiFC analysis in tobacco epidermal cells. Fluorescence indicates interactions between KEGAA-YN (RING mutant lacking E3 ligase activity) and ABI5AAAA-YC (D) or ABI5DDDD-YC (E). Bars = 100 μm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.