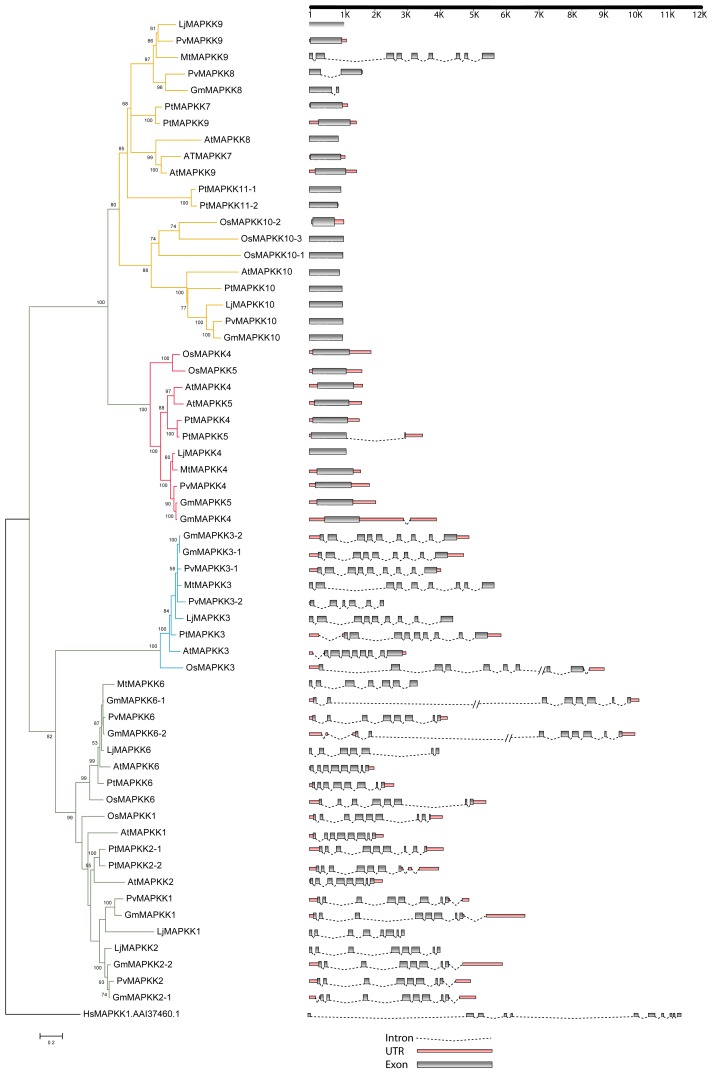
Figure 5. A) Maximum Likelihood analysis of GmMAPKKs and their orthologs in Arabidopsis, poplar, and rice. In the ML phylogram, the values above the branches are bootstrap support of 100 replicates. The JTT+G+I evolutionary model was employed to perform Maximum Likelihood analysis. The MAPKK gene models were accepted for phylogenetic analysis using dual-specificity protein kinases having conserved Aspartate and Lysine residues in their catalytic domain with (D[L/I/V]K) motif and S-X5-T phosphorylation motif along their activation loop. Gene models showing intron/exon lengths (right panel) were mapped onto the phylogram. B) Maximum Likelihood analysis of GmMAPKKs and their orthologs in Arabidopsis, poplar, and rice. In the ML phylogram, the values above the branches are bootstrap support of 100 replicates. The JTT+G+I evolutionary model was employed to perform Maximum Likelihood analysis. The MAPKK gene models were accepted for phylogenetic analysis using dual-specificity protein kinases having conserved Aspartate and Lysine residues in their catalytic domain with (D[L/I/V]K) motif and S-X5-T phosphorylation motif along their activation loop. Gene models showing intron/exon lengths (right panel) were mapped onto the phylogram.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.