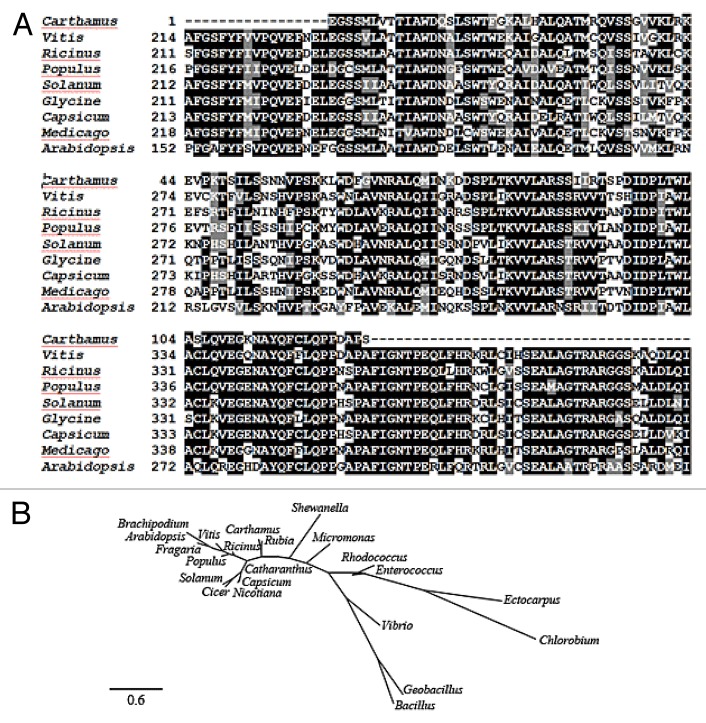
Figure 2. Amino acid sequence alignment (A) and phylogenetic analysis (B) of CtICS orthologs. The known ICS sequences fall into 2 main clusters each devoted to either plants or bacteria. The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Poisson correction method and are in the units of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated from the data set. Phylogenetic tree was constructed at Phylogeny.fr. Accession numbers of sequences are: Carthamus tinctorius (AFI57884), Ricinus communis (XP_002511526), Vitis vinifera (XP_002267681), Populus tremuloides (ACX46384), Fragaria vesca subsp. vesca (XP_004301164), Solanum lycopersicum (NP_001234794), Glycine max (XP_003522193), Capsicum annuum (AAW66457), Arabidopsis thaliana (AAC97926), Cicer arietinum (XP_004514127), Nicotiana tabacum (AAW67000), Catharanthus roseus (Q9ZPC0), Brachypodium distachyon (XP_003578021), Rubia cordifolia (ABK79678), Rhodococcus rhodnii (WP_010837681), Ectocarpus siliculosus (CBN77562), Bacillus cereus (WP_001003908), Micromonas pusilla (XP_003064233), Chlorobium limicola (YP_001944055), Geobacillus thermoglucosidasius (YP_004586325), Enterococcus gallinarum (WP_003127529), Shewanella frigidimarina (WP_011639322), and Vibrio anguillarum (NP_943589). The scale bar indicates 0.6 substitutions per site.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.