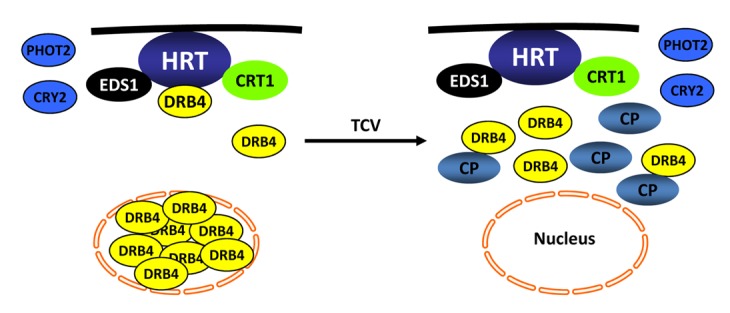
Figure 3. A sketch of components involved in HRT-mediated resistance signaling against TCV. HRT is present on the plasma membrane (shown by black line) and interacts with EDS1, CRT1, and DRB4 proteins. Of these, DRB4 is primarily present in the nucleus, EDS1 is both nuclear and cytoplasmic, whereas CRT1 is on endomembranes. TCV-induced resistance response is initiated in the presence of TCV-CP. Upon recognition of TCV-CP, majority of the DRB4 relocalizes to cytoplasm, where a small pool of DRB4 interacts with CP. The presence of CP also prevents HRT-DRB4 complex formation but has no effect on HRT-EDS1 and HRT-CRT1 interactions. EDS1 potentiates HRT-mediated cell death response and acts redundantly with salicylic acid to regulate HR to TCV. Mutations in DRB4, CRT1, and the blue-light photoreceptors CRY2 and PHOT2, reduce HRT level. Consequently the mutant plants are unable to regulate HR or replication of TCV. No interaction has been detected between CRY2/PHOT2 and HRT, suggesting that these proteins stabilize HRT by inhibiting a negative regulator that mediates degradation of HRT.
