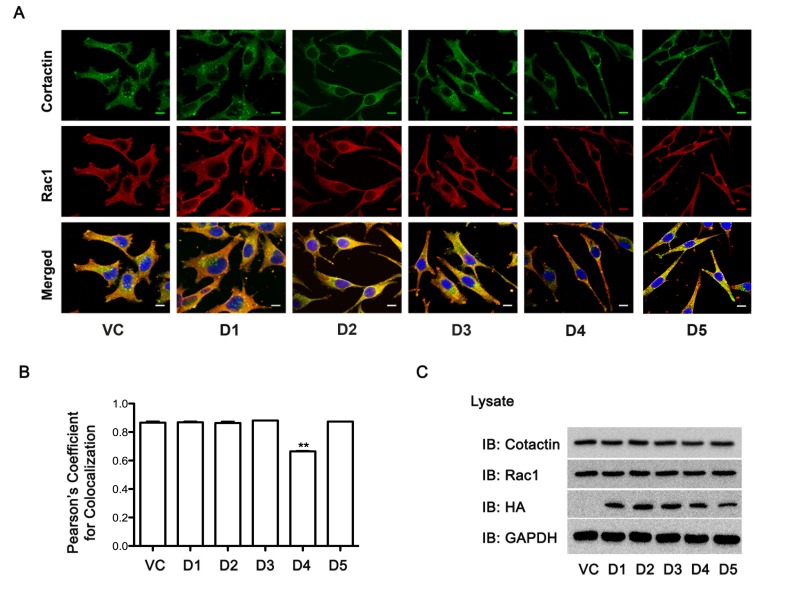
Figure 6. Expression of Rac1-interacting D4 domain of Hax-1 attenuates Rac1-cortactin complex formation.
(A) pcDNA3-SKOV3 vector control cells (VC) and pcDNA3 Hax D1-D5 domain transfected cells (D1, D2, D3, D4, D5) were immunostained with primary mouse monoclonal Rac1 (1:200) antibody for 1h, washed, incubated with Alexa 568-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG for 1h (Red), washed and then stained with Alexa 488-conjugated anti-mouse Cortactin (Millipore, MA) antibody for 1h (Green). Fluorescent micrographs were collected with a Leica SP2 MP Confocal microscope using 63x Plan APO 1.4 NA oil immersion objective. Colocalization of Rac and Cortactin (Yellow) were analyzed, on 3 images for each condition per experiment, using NIH ImageJ software. The scale bar 10 μm is common for all images. (B) For the quantification of Rac1-cortactin colocalization, Pearson's correlation coefficient (PCC) calculated using JACoP (Just Another Colocalization Plugin) for each transfection condition was normalized to the vector control transfection and the average of the normalized PCC is represented as a graph (Figure 6-side panel, lower figure). The statistical significance assessed using one-tailed t-test. ** p<0.05. (C) Lysates (25 μg) from cells transfected with vector-control or vectors encoding Hax-D1-D5 domains were subjected to immunoblot analysis to monitor the expression of HA-tagged Hax-1 domains (D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5), endogenous Rac1, cortactin using the respective antibodies. Equal loading of the lysates was monitored by reprobing the blots with GAPDH antibody. The experiments were repeated at least three times and the presented results are from a typical experiment.