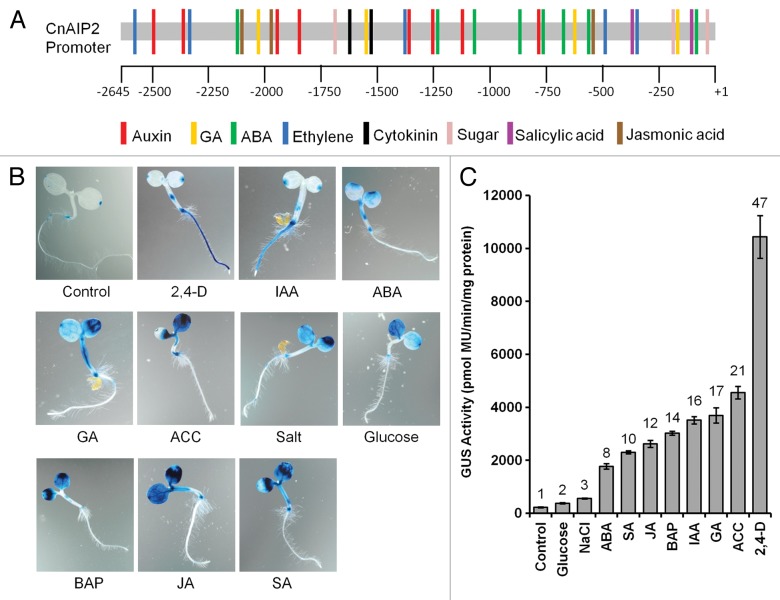
Figure 1.CnAIP2 promoter putative cis-elements and hormonal responses. (A) Putative cis-elements of the CnAIP2 gene promoter analyzed using the online software PLACE (http://www.dna.affrc.go.jp/PLACE/) and PlantCare (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/). Each colored bar represents the approximate position along the promoter of a putative cis-element conferring responsiveness to the indicated hormone. (B) Expression of GUS driven by the CnAIP2 gene promoter as indicated by the GUS histochemical assay using X-gluc as substrate. Staining was conducted over 16 h on 3-d-old seedlings that had been treated for 24 h in a half-strength liquid MS medium containing 5 µM of hormone, 200 mM NaCl, or 6% glucose. The control is shown for 3-d-old seedlings incubated in half-strength MS medium (alone) for 24 h. (C) Enhancement of GUS expression driven by the CnAIP2 gene promoter in seedlings treated as described in (B) as determined by the flurometric activity assay.7 Numbers on bars indicate the fold-increase of GUS activity elicited by each treatment as compared with that of the control (seedlings incubated in half-strength MS medium alone).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.