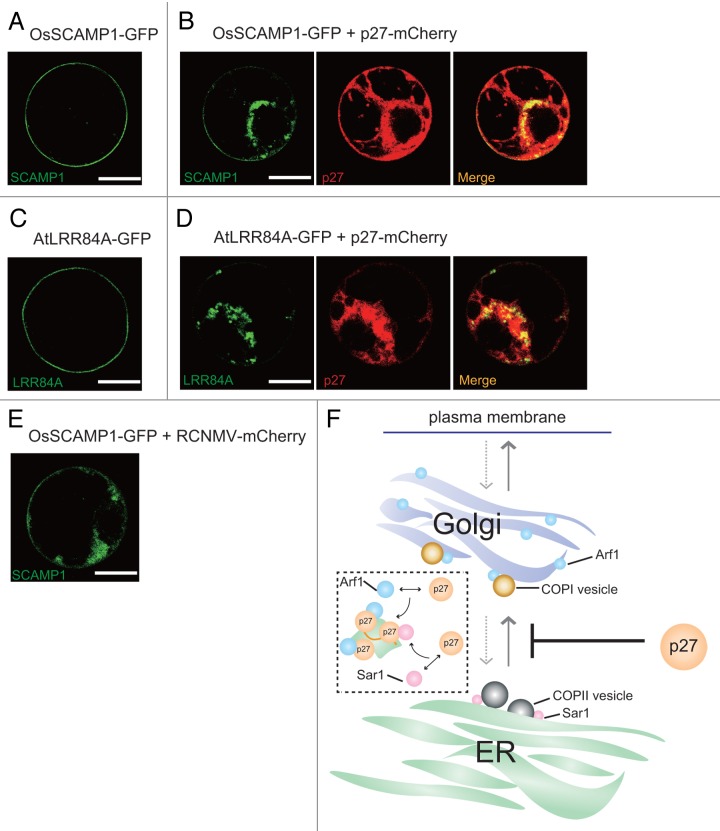
Figure 1. Interference of protein trafficking mediated by dianthovirus p27 replication protein. A plasmid expressing OsSCAMP1-GFP (5 μg) (A and B) or AtLRR84A-GFP (5 μg) (C and D) was cotransfected with a plasmid expressing empty vector (12.5 μg) or p27-mCherry (12.5 μg) into tobacco BY-2 protoplasts. Images were taken at 20 h by confocal laser scanning microscopy. (E) A plasmid expressing OsSCAMP1-GFP (5 μg) was cotransfected with RNA1-mCherry, in which the coat protein open reading frame was replaced by mCherry, and RNA2 into tobacco BY-2 protoplasts. Images were taken at 24 h by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Scale bar = 10 μm. (F) Predicted model of the inhibition step of intracellular trafficking of AtLRR84A and OsSCAMP1 mediated by p27 replication protein. Appropriate trafficking of AtLRR84A and OsSCAMP1 (gray arrows) is likely to be inhibited by p27 at the ER-to-Golgi step. Arf1 and Sar1 are likely to be recruited to viral replication sites from their original compartments (as shown in the dashed-line square). Gray dashed-line arrows indicate retrograde trafficking route. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; Arf1, ADP ribosylation factor 1; Sar1, secretion-associated RAS-related 1; COPI, coat protein complex I, COPII, coat protein complex II.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.