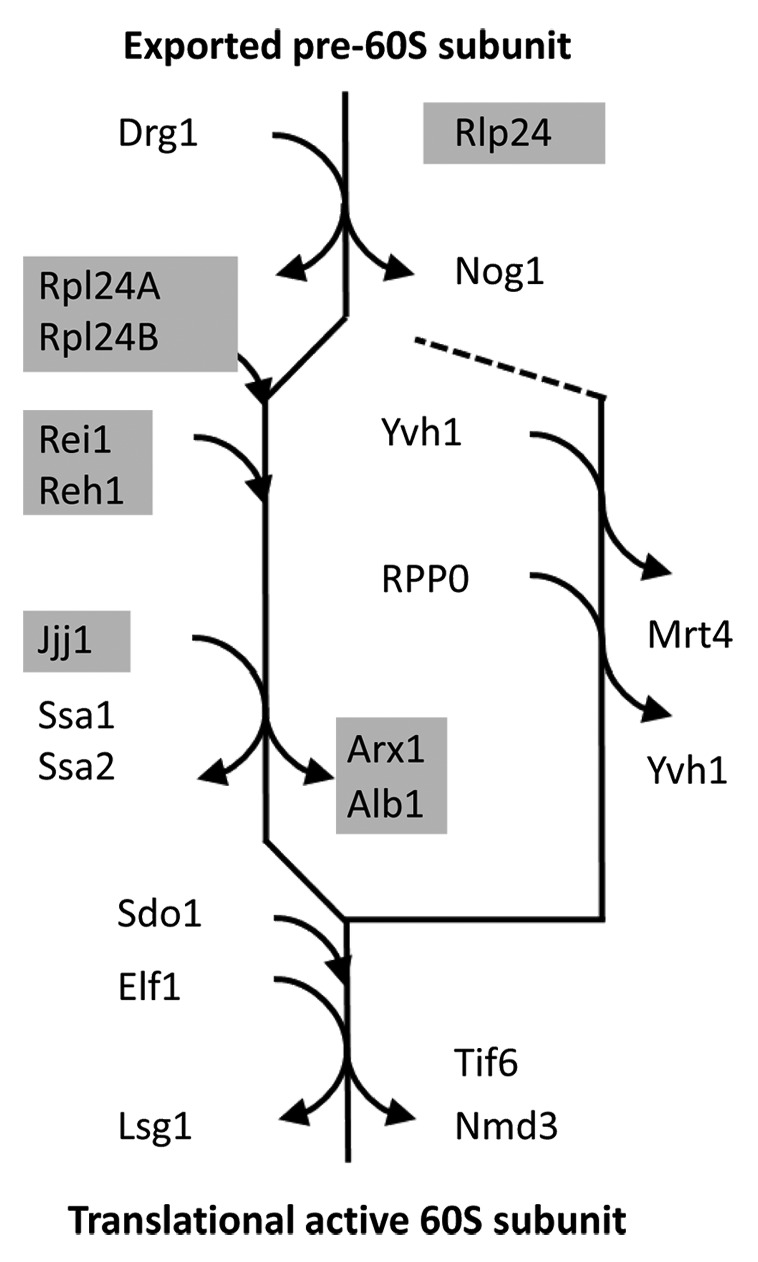
Figure 1. The cytosolic maturation machinery of the 60S large ribosomal subunit from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The flow scheme represents the current model of the cytosolic maturation machinery5 starting with the pre-60S subunit after export from the nucleus (top) and ending with the translational active 60S ribosomal subunit (bottom). The direct mechanistic interaction partners of the yeast Rei1 protein within the model are indicated by light gray underlay. The cytosolic maturation releases inhibitory factors, such as the Arx1/Alb1 complex, Tif6, and Nmd3, (main path on the left) and enables assembly of the ribosome stalk (side branch on the right).
