Figure 2. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) signaling pathway.
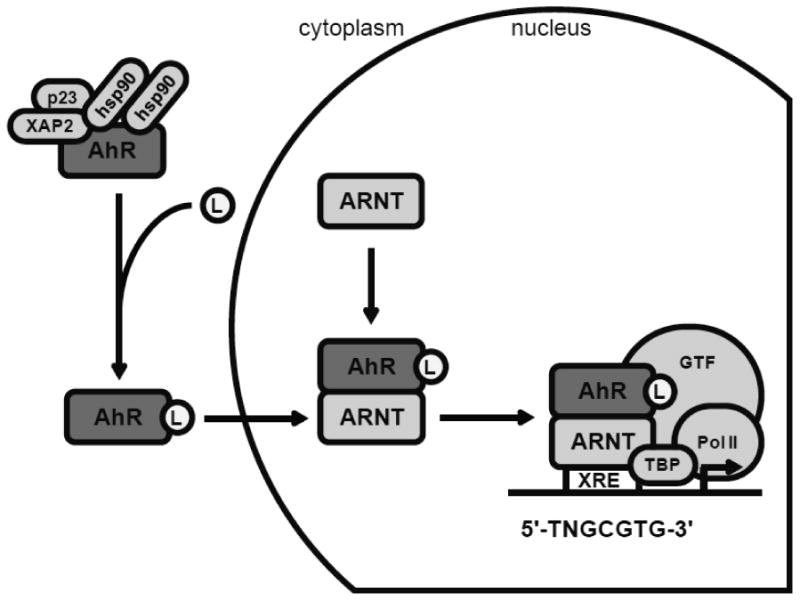
In its quiescent state, the AhR is bound to various repressive factors in the cytoplasm. Ligand (L) binding to the AhR activates the AhR and induces a conformational change which exposes a nuclear localization signal. After nuclear translocation, the AhR dimerizes with ARNT. The AhR: ARNT transcription factor complex binds to XRE sequences in target gene promoters. Interaction with multiple transcriptional coactivators is necessary to induce transcription. GTF: general transcription factors; hsp90: heat shock protein 90; PolII: RNA polymerase II; p23: prostaglandin E synthase 3/ hsp90 co-chaperone; TBP: TATA-box-binding protein; XAP2: AH receptor-interacting protein/ hepatitis B virus X-associated protein 2; XRE: xenobiotic response element.
