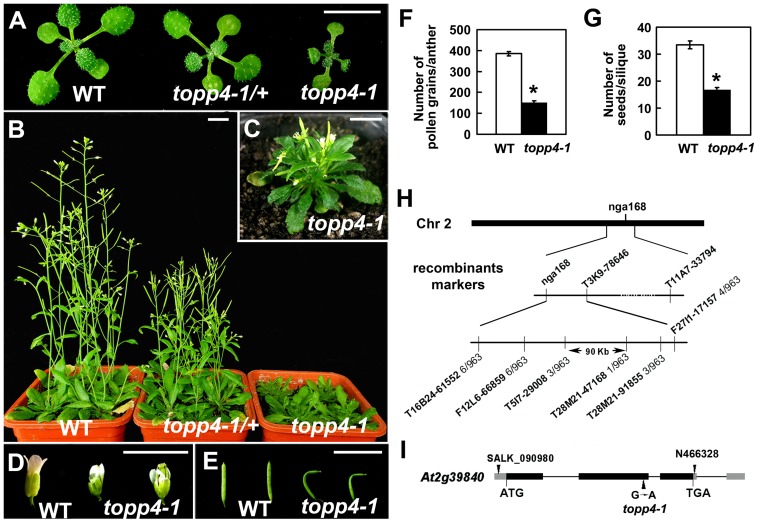
Figure 1. Extremely dwarfed phenotypes of the topp4-1 mutant and map-based cloning strategy of the topp4-1 locus.
(A) Representative 2-week-old wild-type, heterozygous, and homozygous mutant seedlings. (B) Representative 6-week-old plants. (C) A 6-week-old topp4-1 homozygous plant. (D) Flowers from topp4-1 mutant are small with irregular and narrow sepals. (E) Siliques from topp4-1 mutant are twisted with few seeds. (F) Numbers of pollen grains per mature anther are reduced in topp4-1 homozygous plants. (G) Numbers of seeds per mature silique are reduced in topp4-1 homozygous plants. (H) topp4-1 was mapped on chromosome 2. Numbers of recombinants are shown below the markers. (I) Genomic structure of TOPP4. Thick black boxes represent exons and lines between the boxes represent introns. Gray boxes represent untranslated regions. Arrowheads represent three TOPP4 alleles identified through this research (topp4-1) or obtained from other resources (N466328 and SALK_090980). Scale bars = 1 cm. Asterisks in (F) and (G) represent statistic differences based on Student's t test with P<0.05. Error bars in (F) and (G) represent standard error (SE) (n = 30).