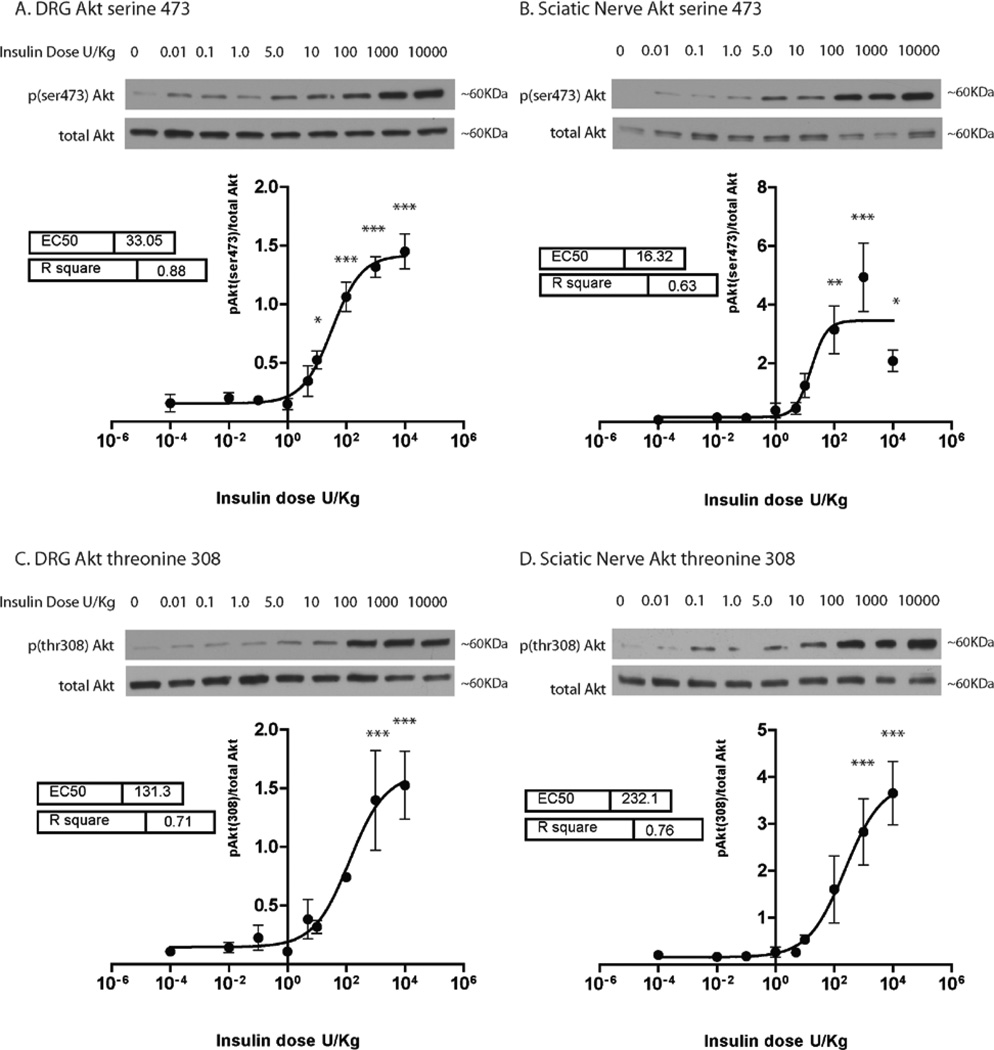
Figure 1. Insulin-induced Akt activation is dose dependent in the DRG and sciatic nerve.
Mice were administered insulin via IP injections at doses of 0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 5.0, 10.0, 100.0, 1,000.0 and 10,000 U/kg. Sterile PBS was used as a vehicle control. 30 min after insulin injection, Akt phosphorylation at sites serine 473 (A and B) and threonine 308 (C and D) were analyzed in the DRG and sciatic nerve and normalized to total Akt levels. Data was fit with a sigmoidal dose response curve and analyzed with a 1-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s post hoc. Results indicate that Akt activation in the DRG (A and C) and sciatic nerve (B and D) increased in a dose dependent manner with insulin. n=4–5 mice per dose. *=p<0.05, **=p<0.01, ***=p<0.001.