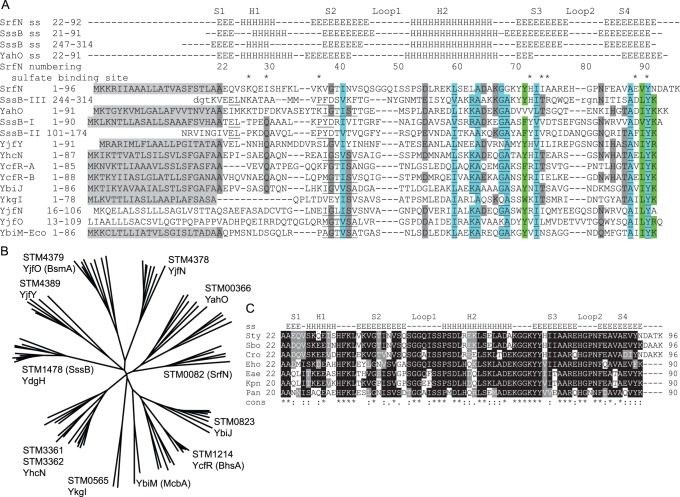
Figure 1. DUF 1471 sequences.
A: Multiple sequence alignment of DUF1471 paralogues from S. Typhimurium, as well as E. coli YbiM, for which there is no close homolog in Salmonella. Alignment of SrfN, YahO, SssB-I and SssB-III is structure-based over the entire structured sequence (SrfN residues 22–91), other alignments are sequence-based and are between core regions only (SrfN residues 35–91) because sequence identity to SrfN residues 22–38 is low and alignments in this region are uncertain. Secondary structure in SrfN, YahO, SssB-I, and SssB-III is indicated above: E = extended (β-sheet) structure, H = helix. The core residues of the sulfate-binding motif in SrfN are indicated with asterisks. Conserved sequence motifs identified by Rudd [1] are underlined. Other conserved residues are highlighted in green or dark grey. Two notable loop regions in the structure are also indicated. SrfN and YahO both have C-terminal tag sequences LEHHHHHH that are not shown. Light grey highlighted portions indicate likely signal sequences for periplasmic localization that are known or likely to be cleaved by a signal peptidase. In the case of SrfN and YahO, the signal sequence was proven experimentally to be cleaved during heterologous expression in E. coli. Inter-domain regions of SssB are not shown. Lower case letters in SssB-III (C-terminal domain) indicate residues with missing electron density in the X-ray structure. Highly conserved residues are indicated by highlighting (blue = hydrophobic, green = polar), somewhat conserved residues are indicated with grey highlighting. The following sequences are listed (S. Typhimurium LT2 locus and UniProt/TrEMBL numbers in parentheses): SrfN (STM0082/Q7CR88), YjfY (STM4389/Q8ZK84), YhcN (STM3361/Q8ZLP6), YcfR seq. I (STM1214/Q8ZQ03), YcfR seq. II (STM3362/Q7CPN0), YahO (STM0366/Q7CR49), YbiJ (STM0823/Q7CQW3), YkgI (STM0565/Q7CR04), YjfO (STM4379/Q8ZK92), YjfN (STM4378/Q8ZK93), SssB (STM1478/Q8ZPL1), YbiM/McbA (E. coli, P0AAX6). B: Unrooted phylogenetic tree (phylogram) constructed from ten diverse genera from the Enterobacteriaceae. Major branches containing Salmonella and E. coli subfamily members are indicated. C: Multiple sequence alignment of SrfN homologues: a subfamily of DUF1471 proteins. For each sequence and abbreviated organism name listed, the full genus and species name, protein/ORF name, database accession number, and similarity to SrfN, excluding the signal sequence, are as follows: Sty, Salmonella enterica Typhimurium, STM0082 (SrfN), NP_459087 and many other Salmonella strains; Sbo, Salmonella bongori, SBG_0068, YP_004728986 (93%); Cro, Citrobacter rodentium, ROD_12311, YP_003364817 (80%); Eho, Enterobacter hormaechei, HMPREF9086_0329, ZP_08496071 (65%); Eae, Enterobacter aerogenes EAE_13230, YP_004592839 (70%); Kpn, Klebsiella pneumonia, KPK_4095, YP_002239898 (68%); Pan, Pantoea sp., Pat9b_3745, YP_004117591 (61%). Notes: Other Salmonella, Klebsiella, and Enterobacter species and strains contain identical or nearly identical sequences to the representatives shown here. However, some Pantoea species do not contain homologues that fall within this DUF1471 subfamily.