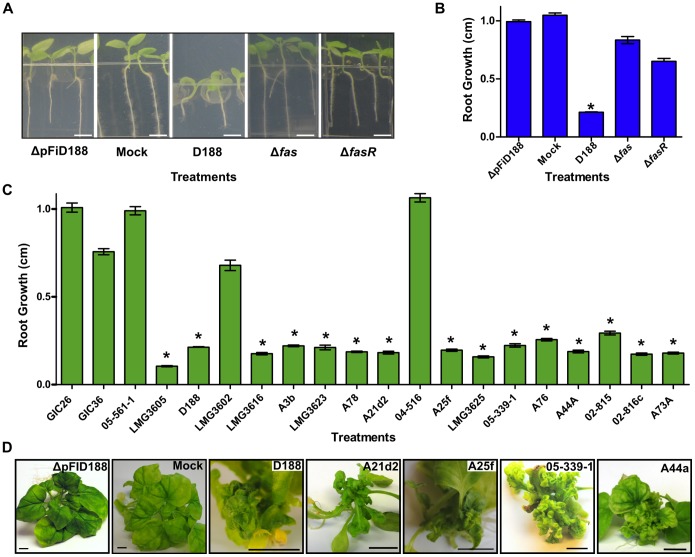
Figure 2. Sequenced isolates of Rhodococcus vary in phytopathogenicity.
(A) Inhibition of N. benthamiana root growth by phytopathogenic Rhodococcus. Seedlings were independently inoculated with D188, its genetic variants, or 10 mM MgCl2 buffer (mock). Photographs were taken at 7 days after inoculation; scale bar = 0.25 cm. (B and C) Average root growth of N. benthamiana seedlings infected with D188 and its genetic variants (B) or with Rhodococcus isolates (C). Root lengths were measured (cm) and averaged. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM); *significant (p-value threshold ≤0.01). All treatments were repeated at least three times with similar results. (D) Isolates of Rhodococcus cause leafy gall disease. N. benthamiana was infected with the ΔpFiD188 strain of D188, mock, or members that represent the diversity of the clade. The black scale bar = 1 cm.