Fig. 2.
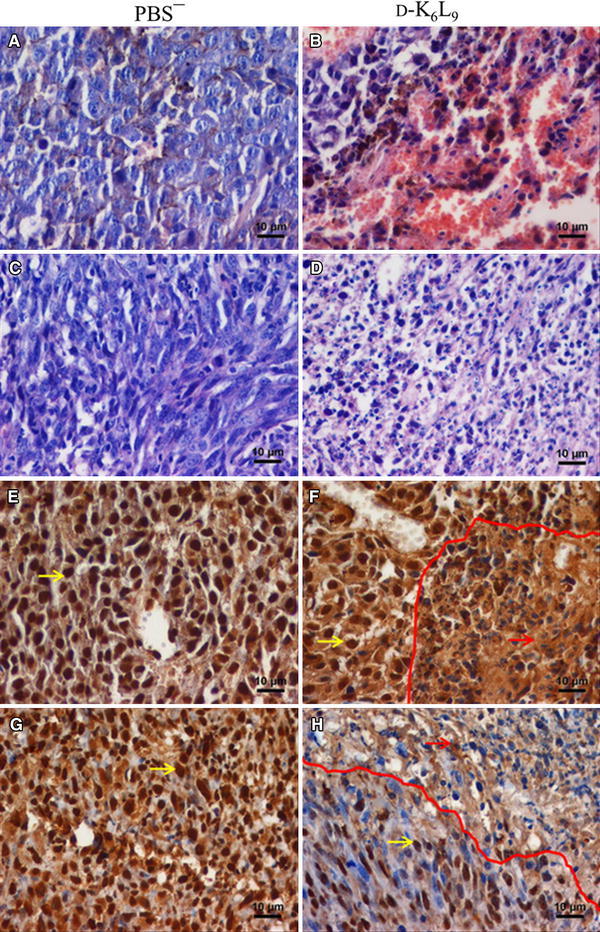
Immunohistochemical assessment of B16-F10 and C26 tumors following therapy with D-K6L9 peptide. Micrographs shows staining of control tumors a, c, e, g (injected with PBS−) and b, d, f, h tumors injected with D-K6L9 peptide. Hematoxylin and eosin staining: a, b B16-F10 and c, d C26. Necrotic areas visible in sections derived from tumors treated with the peptide. Objective lens magnification ×10. Identification of HMGB1: e, f B16-F10 and g, h C26. Brown-colored staining represents HMGB1 protein, cell nuclei are stained blue (hematoxylin). In control tumors, HMGB1 protein is present mainly in cell nuclei (yellow arrows). In tumors injected with D-K6L9 peptide, HMGB1 is present outside of cell nuclei and in extracellular space (red arrows). Red line indicates the border between the area of necrosis and the remaining tissue area. Objective lens magnification ×40
