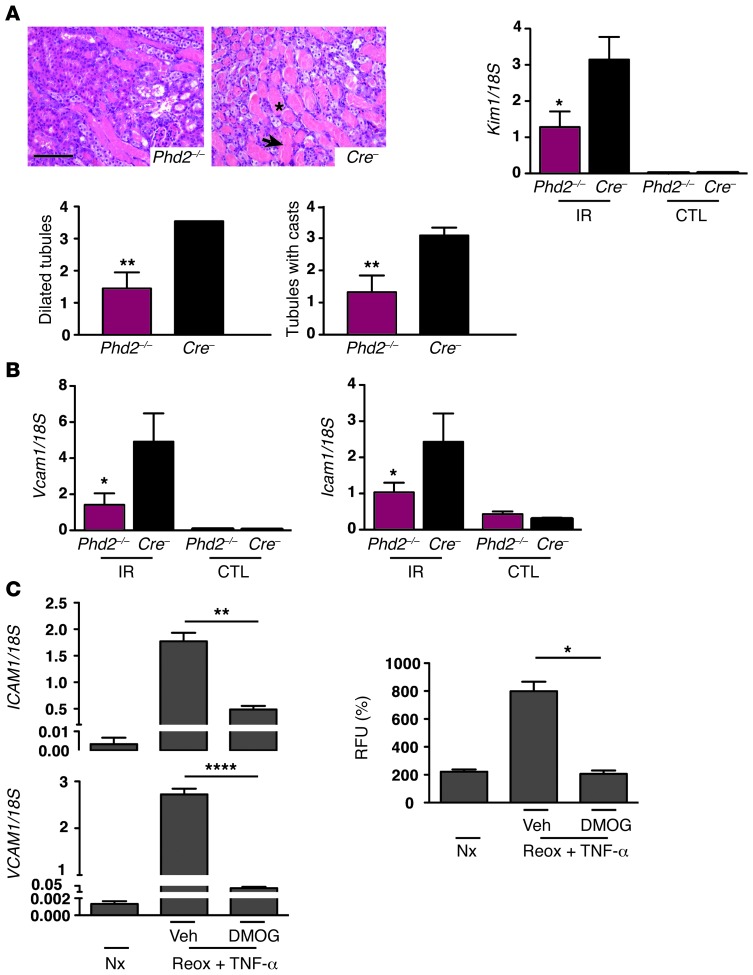
Figure 8. Inactivation of endothelial PHD2 attenuates renal IRI and suppresses the induction of EC-adhesion molecules.
(A) Representative images of H&E-stained kidney sections from Phd2–/– or Cre– littermate controls 3 days after renal IRI. Arrow depicts tubular necrosis. Asterisk indicates cast. Lower graphs show semiquantitative scores for dilated tubules and tubules with cast-forming material (n = 5–7). Kim1 mRNA levels in IR and CTL kidneys are shown on right (n = 5–7). (B) Relative Vcam1 and Icam1 mRNA levels in IR and CTL kidneys on day 3 after IRI (n = 5–7). (C) HUVECs were treated with DMOG or vehicle during hypoxia exposure and subjected to reoxygenation in the presence of TNF-α. Left panels: VCAM1 and ICAM1 mRNA levels in HUVECs. Right panel: functional adhesion assay with fluorochrome-labeled THP-1 cells. THP-1 cells were cocultured for 1 hour with HUVECs; the degree of adhesion is measured in relative fluorescence units. Graph bars represent mean values ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001. Scale bars: 100 μm. veh, vehicle (DMSO).