Figure 2.
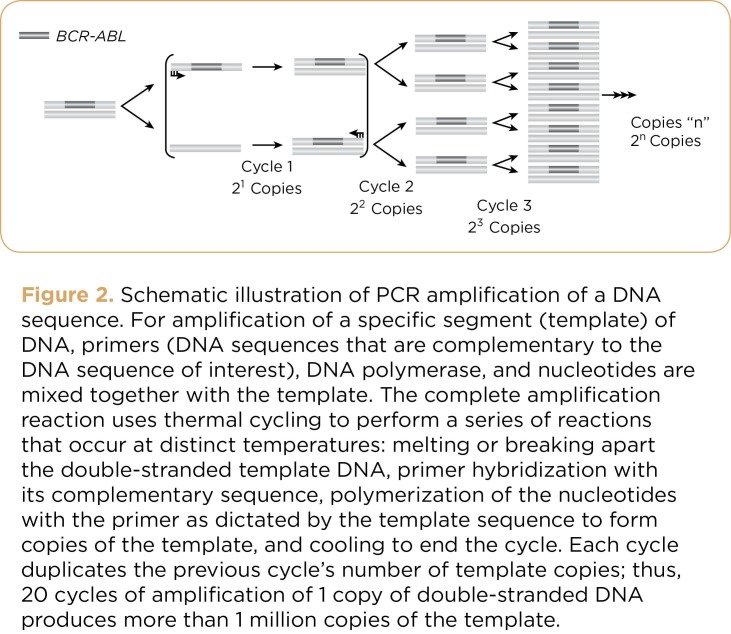
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of PCR amplification of a DNA sequence. For amplification of a specific segment (template) of DNA, primers (DNA sequences that are complementary to the DNA sequence of interest), DNA polymerase, and nucleotides are mixed together with the template. The complete amplification reaction uses thermal cycling to perform a series of reactions that occur at distinct temperatures: melting or breaking apart the double-stranded template DNA, primer hybridization with its complementary sequence, polymerization of the nucleotides with the primer as dictated by the template sequence to form copies of the template, and cooling to end the cycle. Each cycle duplicates the previous cycle’s number of template copies; thus, 20 cycles of amplification of 1 copy of double-stranded DNA produces more than 1 million copies of the template.