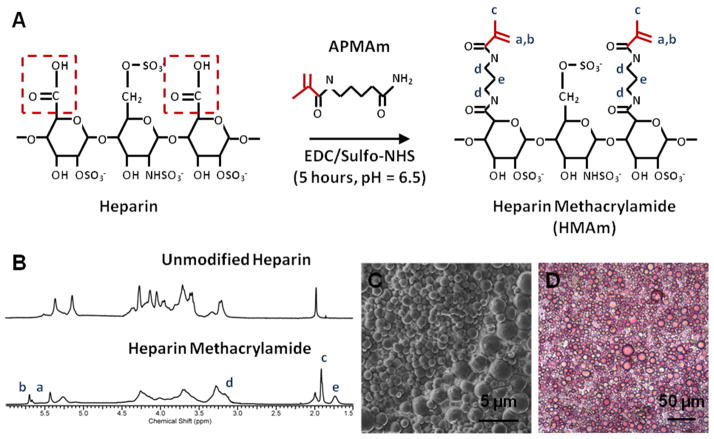
Figure 1. Characterization of Heparin Microparticles.
A) In the methacrylamide substitution reaction, heparin ammonium salt is combined with excess N-(3-Aminopropyl)methacrylamide hydrochloride (APMAm), N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide (sulfo-NHS), and 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC) to produce heparin methacrylamide (HMAm). B) 1H-NMR results indicate that approximately 50% of carboxyl groups on heparin are substituted with methacrylamide groups. Degree of substitution was determined by comparing the integration regions of APMAm protons and unmodified heparin. C) Scanning electron microscopy image of heparin microparticles demonstrates the polydisperse and spherical nature of the microparticles. D) Image of heparin microparticles stained with 1,9-dimethylmethylene blue (DMMB), confirming the presence of heparin.