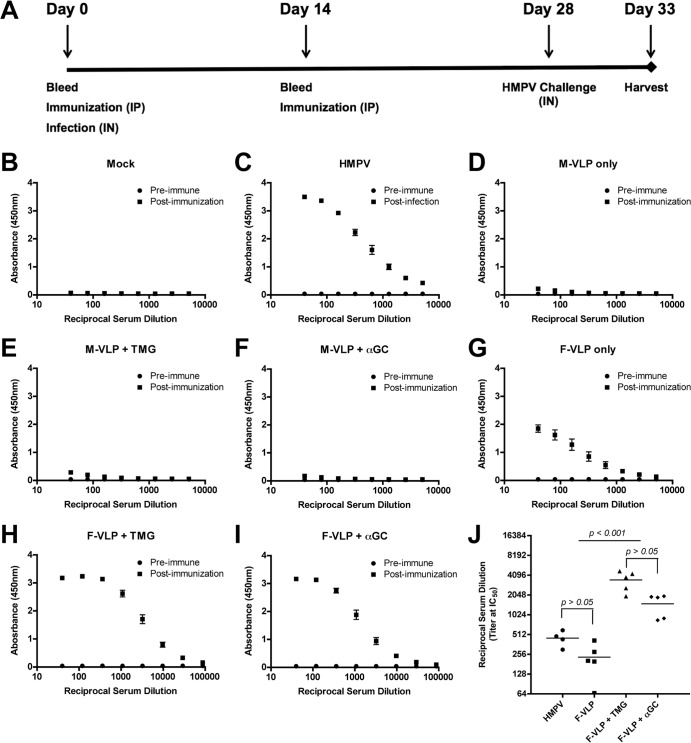
FIG 2.
Immunization with HMPV VLPs induces F-specific antibodies. (A) Schematic showing the immunization protocol. B6 mice (five per group) were immunized two times, 14 days apart, by i.p. injection with VLPs containing either HMPV M (M-VLP) or M plus F (F-VLP) protein. VLPs were administered alone, with TMG adjuvant, or with αGC adjuvant. Negative-control mice were injected with purified supernatant from untreated 293-F cells (mock VLPs). Positive-control mice were infected i.n. with HMPV on day 0. Blood was collected at the time points indicated and at euthanasia to determine the production of F-specific and neutralizing antibodies. (B to J) HMPV F-specific antibody levels in serum samples were measured by ELISA. Preimmune serum was collected on day 0. Postinfection and postimmunization serum samples were collected 5 days after an HMPV challenge. The absorbance resulting from serum antibody binding to plates coated with recombinant F protein is shown for each vaccination group as follows: panel B, mock VLPs; panel C, HMPV; panel D, M-VLP; panel E, M-VLP plus TMG; panel F, M-VLP plus αGC; panel G, F-VLP; panel H, F-VLP plus TMG; panel I, F-VLP plus αGC. Absorbance data are shown as the mean ± the SEM for five mice from three independent ELISAs. Nonlinear regression analyses were performed for groups with F-specific antibodies and used to calculate reciprocal serum titers at half-maximal absorbance (IC50), shown in panel J. Data points represent individual mice, and the bar depicts the mean IC50 titer of each immunization group. Comparisons of multiple groups were made by one-way ANOVA for the P values shown in panel J.