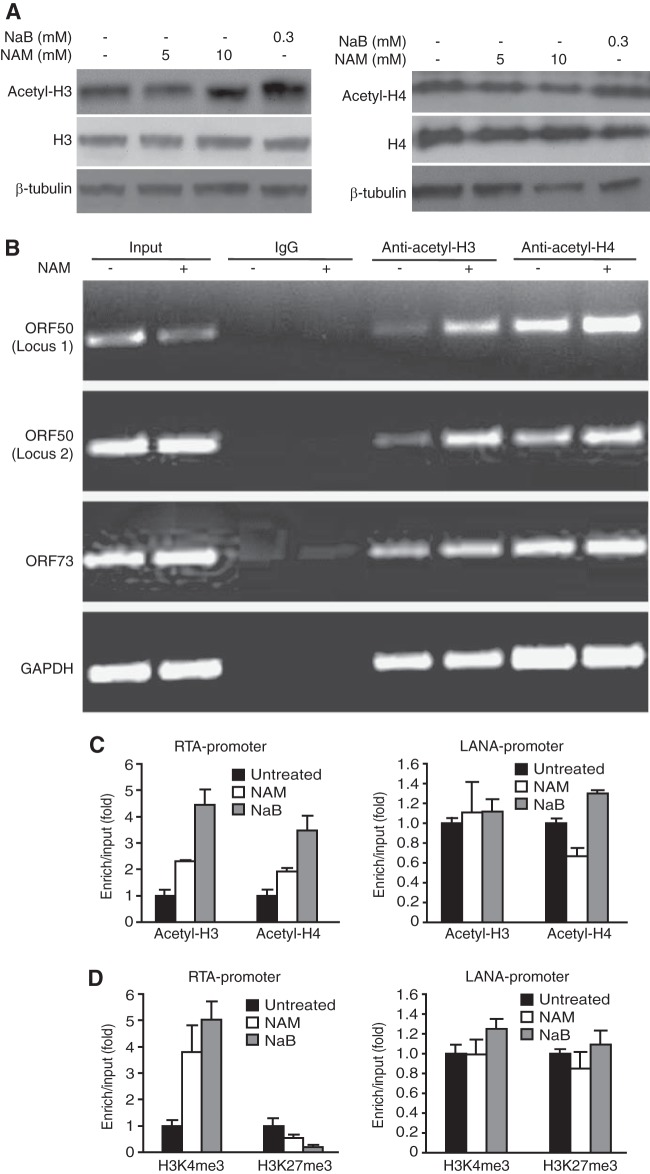
FIG 4.
Treatment with NAM induces the hyperacetylation of histones, increases the level of the active histone H3K4me3 mark, and decreases the level of the repressive histone H3K27me3 mark in the RTA promoter. (A) BCBL-1 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of NAM or 0.3 mM NaB for 24 h and examined for the total and acetylated forms of histone H3 and histone H4 proteins by Western blotting. (B) Quantification of acetylated histones H3 and H4 in RTA and LANA promoters by ChIP-PCR assay. BCBL-1 cells treated with 10 mM NAM for 8 h were subjected to ChIP with an antibody to acetylated histone H3 (anti-acetyl-H3) or histone H4 (anti-acetyl-H4) or a control antibody. The immunoprecipitated DNAs were amplified by semiquantitative PCR for two loci in the RTA promoter, one locus in the LANA promoter, or one locus in the GAPDH intergenic region. (C) Quantification of acetylated histones H3 and H4 in the RTA and LANA promoters by ChIP-qPCR assays. Cells were treated as described in the legend to panel B, and the ChIP DNAs were quantified by qPCR. (D) Quantification of the H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 marks in RTA and LANA promoters by ChIP-qPCR assays. ChIP assays were performed with cells treated as described in the legend to B using an antibody to H3K4me3 or H3K27me3 or a control antibody. The ChIP DNAs were quantified by qPCR.