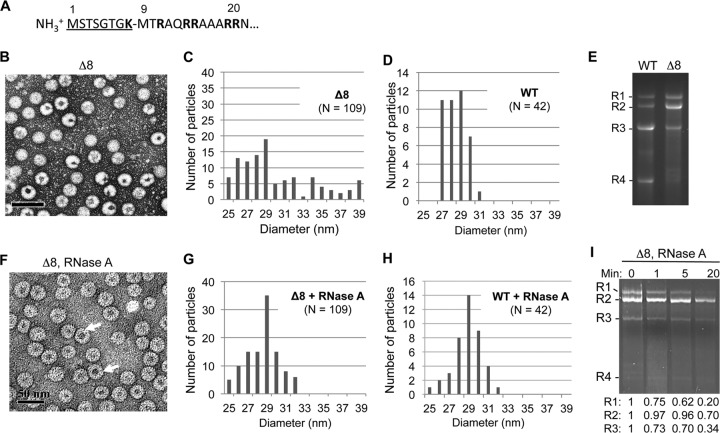
FIG 1.
Deletion of the N-terminal 8 residues of the BMV CP results in the formation of morphologically heterogeneous virions. (A) Sequence of the arginine-rich N-terminal tail of the BMV CP. The residues deleted in mutant Δ8 are underlined. (B) Δ8 virions stained with uranyl acetate exhibit a heterogeneous mixture of virions. (C) Diameters of Δ8 particles visualized by TEM. The virions diameters were measured from micrographs such as those in panel B using the Gatan digital micrograph program. (D) Diameters of WT BMV. (E) RNAs encapsidated by the WT or Δ8 virions. The RNAs were extracted from the virions with the use of phenol-chloroform and were separated on a 1.2% agarose gel in BPTE buffer. The RNAs were denatured by treatment with glyoxal. (F) Δ8 virions stained with uranyl acetate after RNase A treatment. Arrows indicate the locations of virions with larger inner cavities. (G) Diameters of Δ8 particles after treatment with RNase A. (H) Diameter of the WT BMV virions after treatment with RNase A. (I) Abundances of genomic RNAs encapsidated by Δ8 particles after RNase A treatment. The RNAs were extracted as described for panel E and quantified using programs in ImageQuant (Bio-Rad).