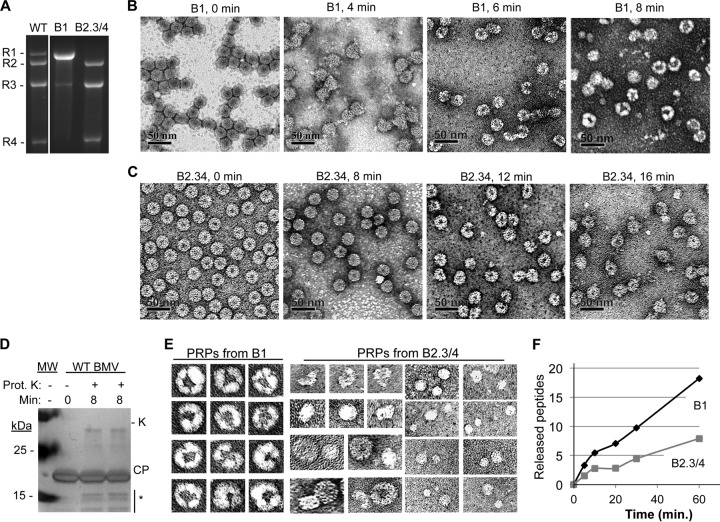
FIG 2.
Separation of BMV virions into subsets and partial proteolysis of the virions. (A) RNAs encapsidated by the B1 and the B2.3/4 virions. WT denotes a sample from a purified preparation that contains all three types of BMV virions. (B) Electron micrographs of B1 virions treated with protease K over an 8-min time course. The virions were stained with uranyl acetate. (C) Electron micrographs of B2.3/4 virions treated with protease K over a 16-min time course. (D) The state of the BMV CP after an 8-min treatment with protease K. The gel image was from an SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie blue. The proteolyzed CPs are identified with an asterisk. Protease K added to the reaction mixture is labeled “K.” (E) Galleries of the four PRPs isolated from the B1 and the B2.3/4 virions. All of the images were adjusted to the same scale. (E) Rate of proteolysis of peptides from the B1 and B2.3/4 virions. Quantities of all of the peptides were determined relative to the amount of protease-resistant bradykinin fragment added to the virions prior to protease treatment. More than 90% of the peptides mapped to the N-terminal 46 residues of the BMV CP. All virions were digested overnight to ensure complete peptide fragmentation (data not shown).