FIG 9.
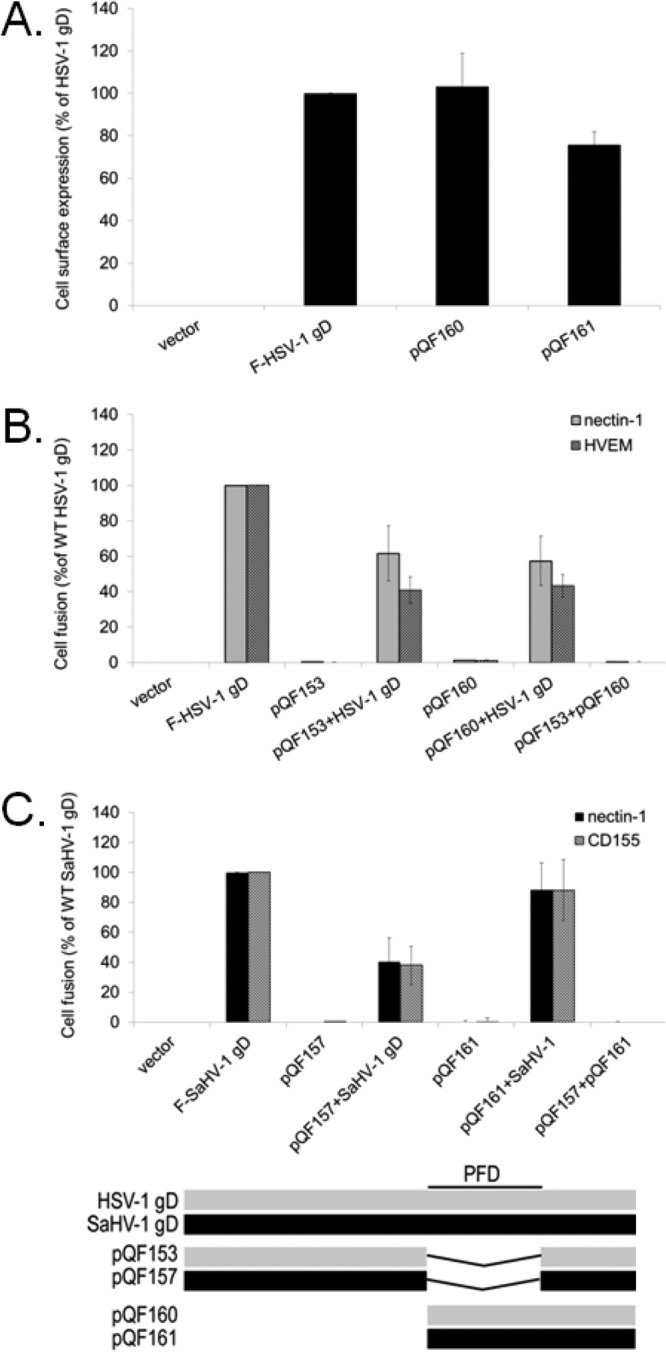
The gD PFD inhibits fusion activity of wild-type gD. (A) Cell surface expression of the PFD-only constructs. The level of surface expression of the HSV-1 and SaHV-1 gD PFD-only mutants was determined by CELISA with effector cells used in the fusion assays below. (B) Target cells were transfected with a plasmid carrying luciferase under the control of the T7 promoter along with nectin-1, HVEM, or empty vector. Effector cells were transfected with plasmids encoding luciferase, gB, gH, and gL from HSV-1, and combinations of wild-type HSV-1 gD, HSV-1 gD with a deletion of the PFD (pQF153), and HSV-1 gD lacking a receptor-binding domain (pQF160). After coincubation of target and effector cells, luciferase activity was measured as an indication of cell-cell fusion activity. (C) Target cells were transfected with a plasmid carrying luciferase under the control of the T7 promoter along with nectin-1, CD155, or empty vector. Effector cells were transfected with plasmids encoding luciferase, gB, gH, and gL from SaHV-1, and combinations of wild-type SaHV-1 gD, SaHV-1 gD with a deletion of the PFD (pQF157), or SaHV-1 gD lacking a receptor-binding domain (pQF161). After coincubation of target and effector cells, luciferase activity was measured as an indication of cell-cell fusion activity. Means and standard deviations of results of three independent experiments are shown for all panels. For clarity, a schematic representation of the constructs is included, with HSV-1 sequence in gray and SaHV-1 sequence in black. Refer to Fig. 4 for a more detailed representation.
