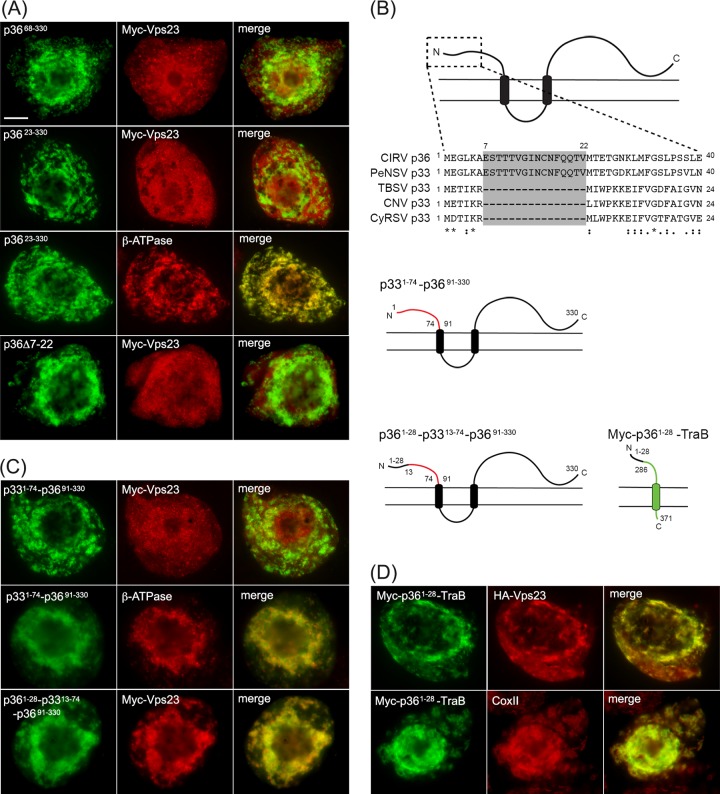
FIG 6.
A unique 16-amino-acid-long sequence at the N terminus of p36 is both necessary and sufficient for relocalizing Vps23 to mitochondria in BY-2 cells. (A) Representative epifluorescence micrographs of BY-2 cells cotransformed with proteins as indicated by panel labels and immunostained (as indicated) for endogenous mitochondrial β-ATPase. Numbers in the name of the construct denote the specific amino acid residues derived from full-length p36 (330 residues) or specific residues deleted from p36. Bar = 10 μm. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of the N termini of various tombusvirus p36 and p33 proteins and cartoon illustrations of p33-36 and p36-TraB hybrid proteins. Sequences were obtained from GenBank and aligned using ClustalW. Identical and similar amino acids in each protein are indicated with asterisks and colons or periods, respectively. The unique amino acid sequence present in CIRV p36 and PeNSV p33 (residues 7 to 22) but absent in TBSV, CNV, and CyRSV p33 are shaded gray. Cartoons depict the structure and topology of p33–p36 and p36-TraB hybrid proteins in the mitochondrial outer membrane. Lines representing amino acid sequences from p33, p36, and TraB are colored red, black, and green, respectively. Numbers represent specific amino acid residues derived from either full-length p33 (296 residues), p36 (330 residues), or TraB (371 residues) and correspond to the numbers in the names of the p33–p36 and p36-TraB hybrid proteins described in panels C and D. (C and D) Representative epifluorescence micrographs of BY-2 cells cotransformed with proteins as indicated by panel labels and immunostained (as indicated) for endogenous mitochondrial β-ATPase. Numbers in the name of the construct denote the specific amino acid residues derived from full-length p36 or p33 and are as illustrated in panel B.