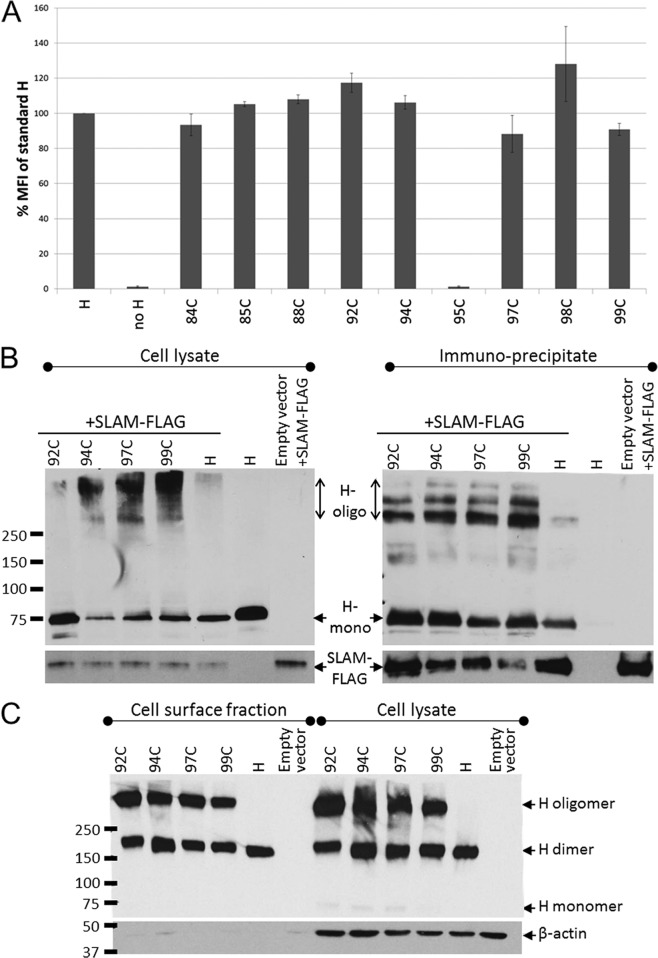
FIG 5.
Cell surface expression and receptor-binding ability of triggering-deficient H-stalk mutants. (A) H-protein cell surface expression measured by FACS analysis. 293T cells transfected with the indicated H construct were stained with an anti-H ectodomain antibody and phycoerythrin-conjugated secondary antibody. The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of each mutant is presented as a percentage of the standard H-protein levels. Error bars indicate standard deviations from three experiments. (B) Receptor-binding ability of H mutants determined by coimmunoprecipitation assay. 293T cells were cotransfected with the indicated H constructs and a SLAM-expressing plasmid (SLAM-FLAG). (Left) Whole-cell lysates of cotransfected 293T cells. (Right) Fraction immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG affinity gel. (Top) Immunoblot probed with an anti-H cytoplasmic tail-specific antibody. (Bottom) Immunoblot probed with anti-FLAG antibody. H-oligo, H oligomer; H mono, H monomer. (C) Immunoblot of a nonreducing SDS-PAGE of the cell surface fraction (left) and corresponding whole-cell lysate (right) of Vero cells transfected with the indicated H constructs.