Figure 3.
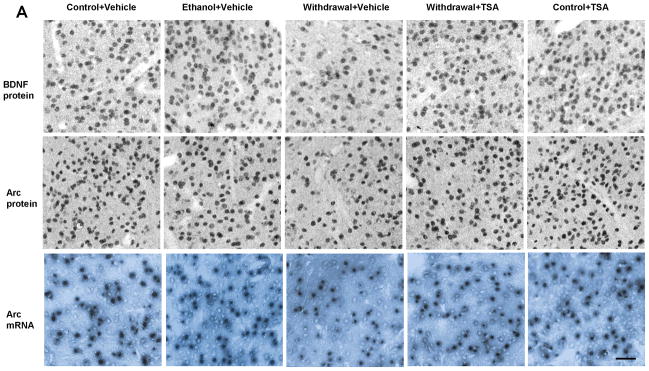
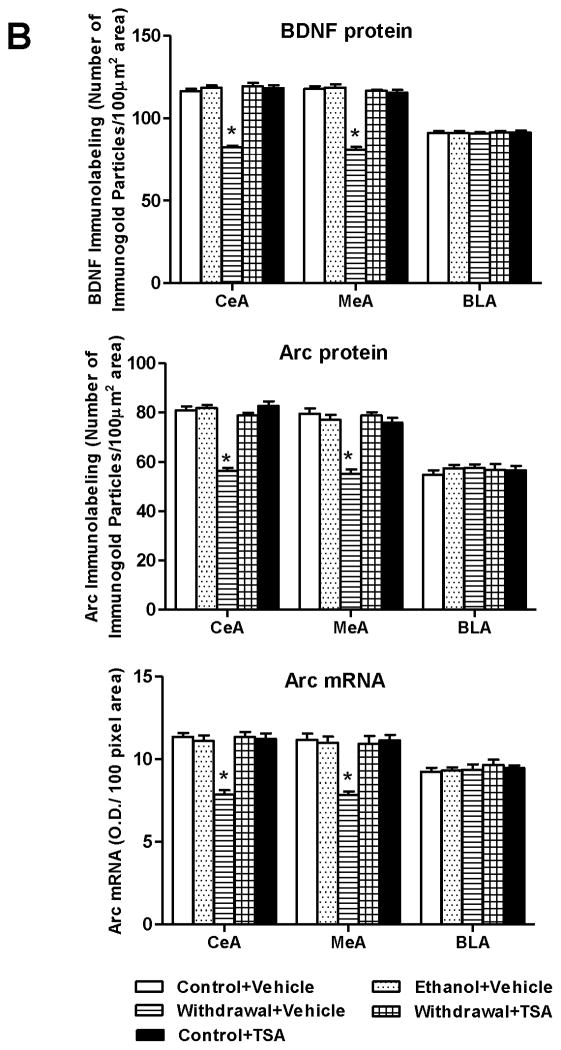
A, Representative photomicrographs of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated (Arc) protein gold-immunolabeling and Arc mRNA in situ RT-PCR in the central nucleus of amygdala (CeA) of various rat groups (Scale bar = 40 μm). B, Bar diagram showing the effects of chronic ethanol treatment and its withdrawal (with or without TSA treatment) on BDNF protein, Arc protein and mRNA levels in CeA, medial nucleus of amygdala (MeA) and basolateral amygdala (BLA) of rats. Values are mean ± SEM of 6 rats in each group. * Significantly different (p <0.001; one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis by Tukey’s test; [BDNF protein: CeA, F4,25=109.11 , p<.001; MeA, F4,25=100.51 , p<.001; Arc protein: CeA, F4,25=60.23, p<.001; MeA, F4,25=29.93, p<.001; Arc mRNA: CeA, F4,25=25.59, p<.001; MeA, F4,25=16.24, p<.001]) from all other groups (Control+ Vehicle, Ethanol+ Vehicle, Withdrawal+ TSA, Control+ TSA injected rats).