Figure 5.
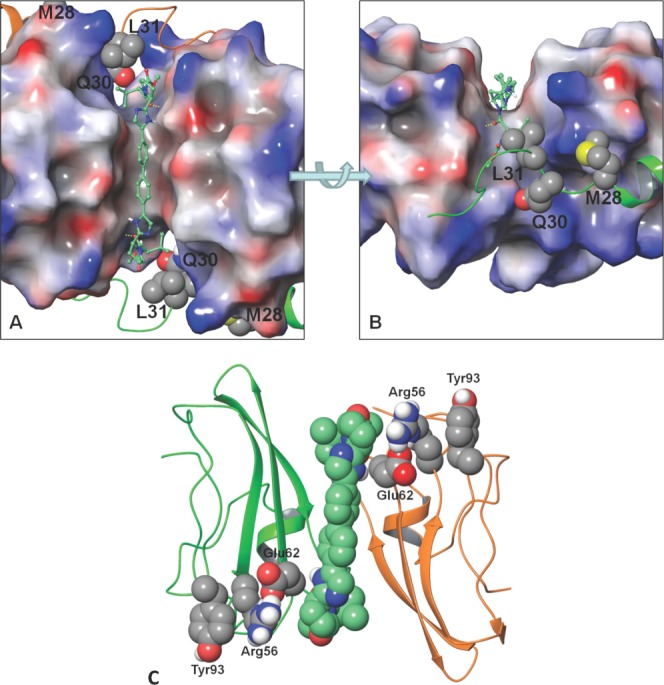
DCV docked into the cleft between the CD dimer. The surface of the dimer is coloured by its electrostatic potential (red is negative, gray is neutral, and blue is positive). The N-terminal residues are shown in ribbon (C-domain in green, D-domain is orange). Key resistant positions are shown with van der Waals surface (carbon: gray, nitrogen: blue, oxygen: red, sulfur: yellow, polar hydrogen: white). DCV is shown in a ball and stick depiction (carbon: aquamarine). A) Top view of DCV docked symmetrically through the cleft. B) Side view focuses on the cap of DCV docked into the cleft. Yellow dotted lines indicate the hydrogen bond between the DCV valine carbonyl and the NS5A Glu62 backbone amide NH. Note: L31 packs against the cap valine moiety of DCV. C) Communication network between DCV and Tyr93. The ribbon depiction of the CD monomer is shown in green and orange, respectively. The van der Waals surface of the DCV (carbon: aquamarine) and the Glu62, Arg56, and Tyr93 (carbon: gray) communication network. Use this link to access the interactive version of this figure.
