Figure 5.
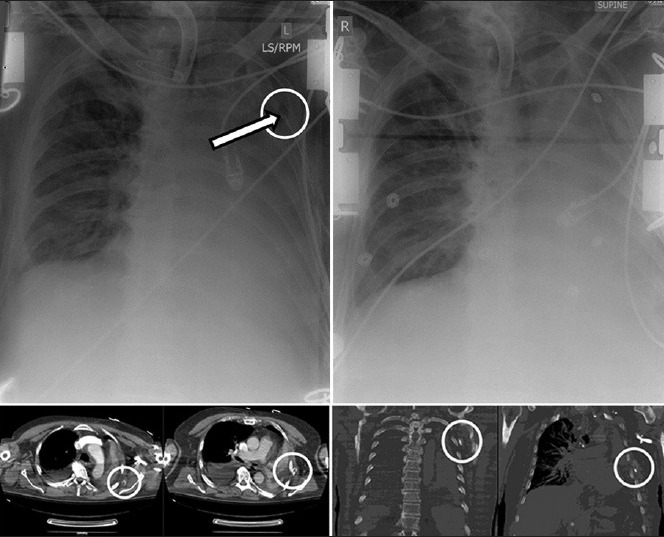
Subcutaneous chest tube placement in a patient with a large left-sided hemothorax. Immediately upon tube thoracostomy placement, large amount of sanguineous effusion was liberated. The patient was also noted to have an air leak in the suction apparatus. The initial chest radiograph (top left) was difficult to interpret due to ECG wires interfering with proper visualization, but the tip of the chest tube (arrow) was determined to be intrathoracic. Despite improved clinical picture, both the TT drainage and the air leak quickly stopped. The subsequent CT scan shows the TT to be extrathoracic (bottom images). A new chest tube was promptly inserted and the initial chest tube removed (top right).
