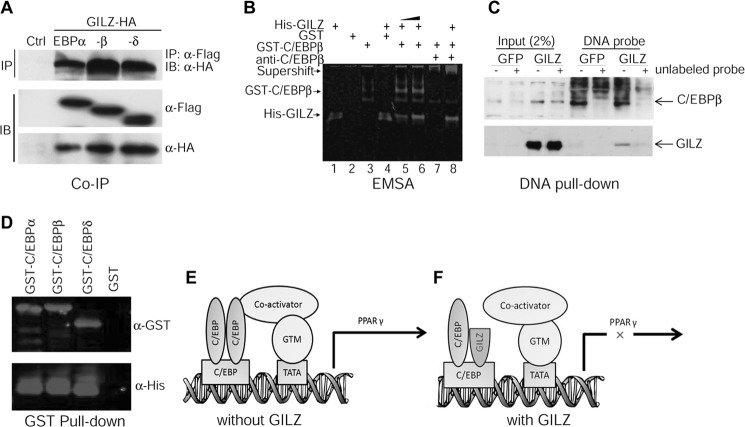
FIGURE 7.
GILZ interacts with C/EBPs. A, co-immunoprecipitation assay. 293T cells were cotransfected with HA-GILZ and Flag-C/EBPα, -β, or -δ. Whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag and detected with anti-HA antibody to show co-precipitated GILZ protein. The expression of C/EBPs and GILZ in transfected cells is shown by Western blots using anti-Flag antibody and anti-HA antibody, respectively. B, EMSA. Affinity-purified GST-C/EBPβ and His-GILZ protein was incubated with a 30-bp IRDye-labeled DNA probe containing tandem repeat C/EBP binding site either alone (lanes 1 and 3) or together (lanes 5, 6, and 8). The DNA-protein complex was resolved in native polyacrylamide gel and imaged using an Odyssey Infrared Imaging System. Lane 1 contains 8 μg of His-GILZ, lane 2 contains 8 μg of GST, lane 3 contains 0.5 μg of GST-C/EBPβ, lane 4 contains 8 μg of GST plus 8 μg of His-GILZ, lanes 5–8 contain 0.5 μg of GST-C/EBPβ plus His-GILZ (8 and 12 μg in lanes 5 and 6, respectively). Lane 7 contains 0.5 μg of GST-C/EBPβ and 2 μl of anti-C/EBPβ antibody. Lane 8, contains the same as lane 7 plus 8 μg of His-GILZ. C, DNA pulldown assay showing interactions between GILZ, C/EBPβ, and PPARγ promoter. Cell lysates harvested from GILZ- and GFP-expressing MSCs were incubated with biotin-labeled DNA probe mentioned above, and the protein-DNA complex was purified with magnetic beads conjugated to avidin. The complex was separated on SDS-PAGE, transferred onto membrane, and then detected with antibodies against C/EBPβ or GILZ. The specificity of protein-DNA interaction was confirmed by adding 60× excess of unlabeled DNA probe as indicated. D, GST pulldown assay showing interaction between GILZ and C/EBPs. Purified GST-C/EBPs were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads and then incubated with His-tagged GILZ; after several washes, the bound proteins were eluted by boiling in sample buffer, separated by SDS-PAGE, and detected with anti-GST or anti-His antibodies. E and F, working model illustrating how GILZ may inhibit C/EBP-mediated PPARγ gene transcription. In the absence of GILZ (E), dimerized C/EBPs bind to C/EBP-binding sites and associate with co-activators such as PGC-1 and initiate transcription. However, in the presence of GILZ (F), the association of C/EBPs with co-activators and general transcription machinery (GTM) is disrupted, thus C/EBP-mediated PPARγ gene transcription is inhibited. IB, immunoblot; IP, immunoprecipitation;